SATELLINE-EASy Pro 35W
User Guide v.1.4
92
if the data transmission protocol is well prepared for this and the data transmission that
occasionally slows down does not cause any problems to the system.
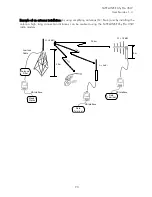
Vertical polarised antennas (antenna elements are in vertical position) are often used in radio
systems. In a system between a base station and substations vertical polarisation is recommended.
The radio modem antenna cannot be mounted on the same level as the other substation
antennas in the same building. The best way to distinguish from the other antennas situated in the
neighbourhood is to mount the antennas as far as possible from each other on the altitude level.
The best result is generally obtained when all the antennas are in the same mast. With an extra
ground plane between the antennas more distinction can be obtained between the antennas in
the mast.
Horizontal polarisation can be used in data transmission between two points. With the
polarisation attenuation more distinction is obtained to vertical polarised systems. The influence of
the directional patterns of the antennas must, however, be taken into consideration. If a distinction
to another interfering antenna is wanted with the horizontal polarised antennas there must be a
good attenuation of the back lobe. In addition to this the interfering radiator should be situated
behind the antenna.
When a system does not demand the use of an omni-directional antenna it is recommended that
directional antennas are used e.g. two-element yagis in permanent external installations. Please
note that as antenna amplification increases the setting of the direction of the antenna requires
more attention.
Base stations in high places should be supplied with high-Q cavity filters. Please note that the
higher the base station antenna, the larger the coverage area and in turn that the risk of
interference is also increased.
SATEL recommends the use of a band-pass filter with a large Q in the antenna cable of the base
station.