S&C Instruction Sheet 1072-530
35
SpeedNet Client Tool
NOTICE
A login from the SpeedNet Client Tool is somewhat different from other logins, such as telnet
or remote desktop sessions. The communication between the client tool and the radio is
fundamentally transactional. When the user logs in using the SpeedNet Client Tool, the client
tool contacts the radio via SNMPv3/UDP/IP using the username and password credentials
provided, and attempts to fetch the radio’s configuration information. If the credentials are
incorrect, the client tool informs the user that the login failed. If the credentials are correct,
the client tool displays basic configuration information just fetched in the upper right corner
of the Main window, and shows the Status as connected. Each subsequent transaction,
until the client tool is directed to a new radio, is individually authenticated via SNMPv3
using the credentials provided by the user at the start of the session and stored in the client
tool. No state of the SpeedNet Client Tool session is stored in the radio, and the client tool
does not poll the radio to update displayed information between user transactions. Thus,
the radio can have several client tools from different PCs logged in at the same time. Also,
the radio can undergo changes such as a reboot behind the client tool session with no
impact on the client tool, except that transaction attempts (e.g. changing to another client
tool tab or clicking an
Apply button) during the reboot will not function.
Interfaces Window,
Ethernet Tab
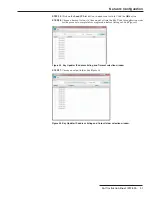
Figure 63. Configuration of the Ethernet interface.
Figure 63 shows the
Ethernet Interface
confi guration window. On a given SpeedNet
Radio mesh, the confi gurations of all the Ethernet interfaces should differ so there is no
overlap between the Ethernet port subnets or between the Ethernet port subnets and
the wireless subnet.
Redundancy for SpeedNet Head-End Radios and SpeedNet Gateways is supported
using the Ethernet interface (and not the Wireless interface). This redundancy feature
provides fault tolerance to head-end radios (with the
AODV Gateway
mode on or off),
and only applies to non-serial configurations. Because a single head-end radio is a single-
point of impairment, redundancy improves communication reliability. This is important
for head-end radios because they are the link to the customer enterprise network.