REHAU has performed extensive testing of RAUPEX pipes exposed to
UV, leading to the maximum UV exposure times expressed in
accumulated days. Once the pipes leave the manufacturing plant, any
exposure to UV, including transportation and storage, is part of the
accumulated exposure time.
Although ASTM F876 only categorizes up to 6 months of UV resis-
tance (Material Designation Code = 3
3
06), REHAU has tested and
certi
fi
ed RAUPEX white UV shield pipe according to ASTM F2657 for
the following maximum UV exposure period:
- RAUPEX white UV shield pipe: Maximum exposure time of one year
accumulated
RAUPEX pipes must be kept in the original packaging until the time of
installation. RAUPEX must not be stored outdoors and is not designed
for permanent outdoor exposure (with the exception of non-exposed
buried applications).
NOTICE
Failure to follow maximum UV exposure limits may damage the pipe
resulting in leaks and operational failures, and will negate any
warranty provided by REHAU for RAUPEX pipes.
4.9 Bend Radius
RAUPEX pipe may be bent, even when cold. REHAU support bends
can assist to create tight bends without kinking. The typical bend
radius used by the installer is 8X the OD. The minimum bend radius is
5X the OD for cold bends. For an even smaller bend radius, the pipe
may be heated with a heat gun and bent to no less than 3X the OD. If
a tighter bend radius is required, the designer should consider using a
smaller diameter pipe.
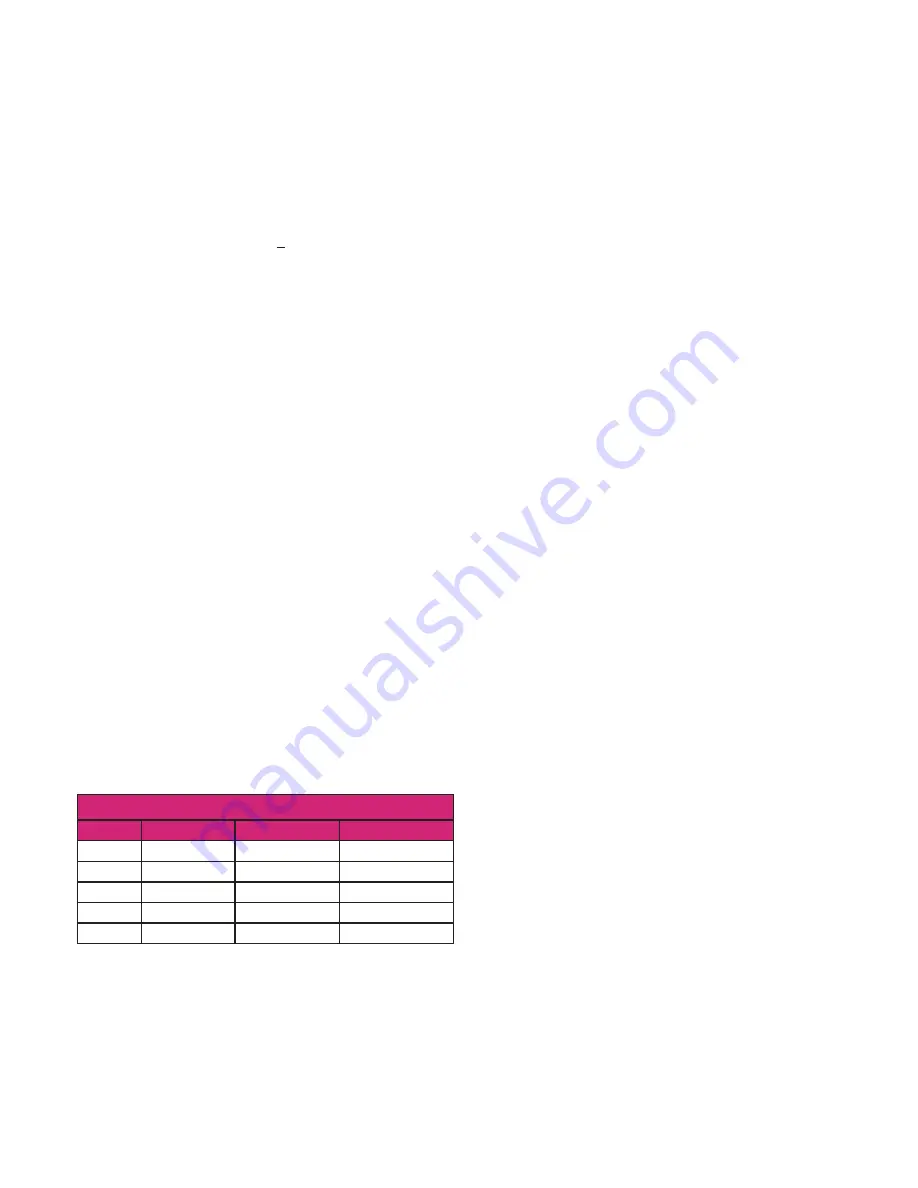
Table 4.4: RAUPEX Bend Radius
Bend Radius in (mm)
Pipe Size
Typical 8X OD
Min. Cold 5X OD
Min. Heated 3X OD
3/4 in
7.0 (178)
4.375 (111)
2.625 (67)
1 in
9.0 (229)
5.625 (143)
3.375 (86)
1 1/4 in
11.0 (279)
6.875 (175)
4.125 (105)
1 1/2 in
13.0 (330)
--
--
2 in
17.0 (432)
--
--
4.10 Chemical Compatibility
While RAUPEX pipes are resistant to many chemicals that are used in
typical residential
fi
re sprinkler applications, there are some chemicals
that may damage the pipe.
Chemicals that may be damaging include (but are not limited to):
- Adhesives
- Oil or petroleum-based products
- Paints
- Solvents
- Oxidizing agents
- Disinfectants
- PVC glues
- Solvents and cements
Many factors, such as exposure time, temperature, pressure and other
operating parameters, can in
fl
uence the performance of a pipe that is
exposed to a chemical. To determine the impact of a particular
chemical, short- and long-term pressure testing may be required. In
some cases, a pipe may be resistant to short-term exposure to the
chemical, but not resistant to continuous exposure. Each chemical
must be evaluated individually. It is the responsibility of the installing
contractor to verify chemical compatibility of any chemicals when
coming into contact with the polymer material.
4.11 Freeze Break Resistance
The
fl
exibility of the RAUPEX pipe allows it to expand as water freezes
in the pipe as long as the pipe has room to expand. When the water
thaws, the pipe returns to its original shape. If the pipe is not allowed
to expand (e.g., it is encased in concrete), it may burst.
NOTICE
Designers and installers must take precautions as per the guidelines
de
fi
ned in NFPA 13D to ensure that pipes do not freeze. Frozen pipes
may burst resulting in leaks and operational failures.
4.12 Condensation
Condensation occurs on pipes when the surface temperature is lower
than the dew point of the environment. This is typically a problem for
metallic cold water piping. PEX pipe has a lower thermal conductivity
(0.41 W/m°K) than copper (401 W/m°K) resulting in less heat loss to
the surface and greater resistance to condensation or sweating.
10











































