Glossary
Glossary-2
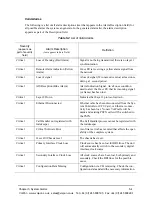
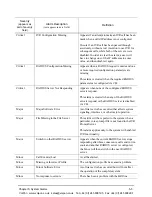
Intranet communication. Communication within the
same company, usually through an Ethernet hub.
IP Address. A unique 32 bit address that identifies a net-
work device is connected to the network via TCP/IP.
IVR. Interactive Voice Response enables you offer ser-
vices, such as Pre-paid calling cards and Post-paid
accounts to your customers.
L
LAN. Local Area Network. A local area network that
carries data between workstations in the same loca-
tion. Workstations in a LAN are connected togeth-
er— typically by an Ethernet hub— to share
information.
LEDs. Indicators as to the status of the chassis and other
components of the system. LEDs appear on the chas-
sis and other components.
M
Maintenance Mode. A CLI module which provides util-
ities for maintaining the system.
Monitor Module. A CLI module which provides a set of
utilities to monitor the network and all system com-
ponents.
N
NT-1. Network Termination Type 1. Device that is re-
quired to connect ISDN terminal equipment to an
ISDN line.
Null modem cable. A 9-pin cable used to connect the
Tenor BX
to a PC’s asynchronous console port.
P
PacketSaver. A packet multiplexing technology which
reduces the amount of IP bandwidth require to sup-
port multiple calls flowing between two networks.
PBX. Private Branch Exchange. Telephone switch locat-
ed on a customer’s premises that establishes circuits
between users and the PSTN (public network).
Point-to-Point. A single Terminal Equipment is connect-
ed to the NT1 which can be up to 1000m away.
Power Inlet. Inlet for which you insert the supplied AC
power cord. The unit requires a 110-220 VAC.
PSTN. Public Switched Telephone Network (also known
as Central Office). Telephone Company Switching
facility.
R
RJ-45. A CAT 5 cable used to connect the
Tenor BX
to
an Ethernet, Line Circuit or Trunk Circuit.
RADIUS. When using IVR, the RADIUS (Remote Au-
thentication Dial-In User Service) is used for authen-
ticating and authorizing user access to the VoIP
network.
S
SelectNet
™.
The next generation of TASQ technology;
the functionality monitors your data network for jit-
ter, latency, and packet loss, and transparently
switches customer calls to the PSTN when required.
SIP. A signaling protocol used to establish a session on
an IP network.
SNMP. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
is the standard protocol used to exchange network in-
formation between different types of networks.
S/T interface. A four-wire ISDN interface. Runs from
TE1 devices to NT.
Subnet Mask. An IP address that determines how an IP
address is divided into network and host portions ac-
cording to the bits.
T
TA. Terminal Adapter. Adapter that allows a TE-2 termi-
nal to connect to an ISDN user-network interface.
TE-1. Terminal Equipment type 1. Uses an interface that
complies with the ISDN user-network interface re-
commmendations. This device can connect and work
with ISDN.
TE-2. Terminal Equipment type 2. This equipment uses
an interface that complies with interface recommen-
dations other than the ISDN interface recommenda-
tions. This device requires a terminal adapter to
connect and work with ISDN.
W
WAN. Wide Area Network. A number of LANs connect-
ed together through a long distance communications
medium. For example, your company may have a
LAN in New York, a LAN in Tokyo, and a LAN in
Los Angeles. When these sites connect together over
VoIPon www.voipon.co.uk [email protected] Tel: +44 (0)1245 808195 Fax: +44 (0)1245 808299