Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.
5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Index of this chapter:
5.1 Test Points
5.2 Service Modes
5.3 Stepwise Start-up
5.4 Service Tools
5.5 Error Codes
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.7 Protections
5.8 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
5.9 Software Upgrading
5.1
Test Points
As most signals are digital, it will be difficult to measure
waveforms with a standard oscilloscope. However, several key
ICs are capable of generating test patterns, which can be
controlled via ComPair. In this way it is possible to determine
which part is defective.
Perform measurements under the following conditions:
•
Service Default Mode.
•
Video: Colour bar signal.
•
Audio: 3 kHz left, 1 kHz right.
5.2
Service Modes
Service Default mode (SDM) and Service Alignment Mode
(SAM) offers several features for the service technician, while
the Customer Service Mode (CSM) is used for communication
between the call centre and the customer.
This chassis also offers the option of using ComPair, a
hardware interface between a computer and the TV chassis. It
offers the abilities of structured troubleshooting, error code
reading, and software version read-out for all chassis.
(see also section “
”).
Note:
For the new model range, a new remote control (RC) is
used with some renamed buttons. This has an impact on the
activation of the Service modes. For instance the old “MENU”
button is now called “HOME” (or is indicated by a “house” icon).
5.2.1
Service Default Mode (SDM)
Purpose
•
To create a pre-defined setting, to get the same
measurement results as given in this manual.
•
To override SW protections detected by stand-by
processor and make the TV start up to the step just before
protection (a sort of automatic stepwise start-up). See
section “
•
To start the blinking LED procedure where only LAYER 2
errors are displayed. (see also section “
”).
Specifications
Table 5-1 SDM default settings
•
All picture settings at 50% (brightness, colour, contrast).
•
All sound settings at 50%, except volume at 25%.
•
All service-unfriendly modes (if present) are disabled, like:
–
(Sleep) timer.
–
Child/parental lock.
–
Picture mute (blue mute or black mute).
–
Automatic volume levelling (AVL).
–
Skip/blank of non-favourite pre-sets.
How to Activate SDM
For this chassis there are two kinds of SDM: an
analog
SDM
and a
digital
SDM
. Tuning will happen according
•
Analog
SDM
: use the standard RC-transmitter and key in
the code “062596”, directly followed by the “MENU” (or
HOME) button.
Note:
It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main
menu will appear. To switch it “off”, push the “MENU”(or
HOME) button again.
•
Digital
SDM
: use the standard RC-transmitter and key in
the code “062593”, directly followed by the “MENU” (or
HOME) button.
Note:
It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main
menu will appear. To switch it “off”, push the “MENU” (or
HOME) button again.
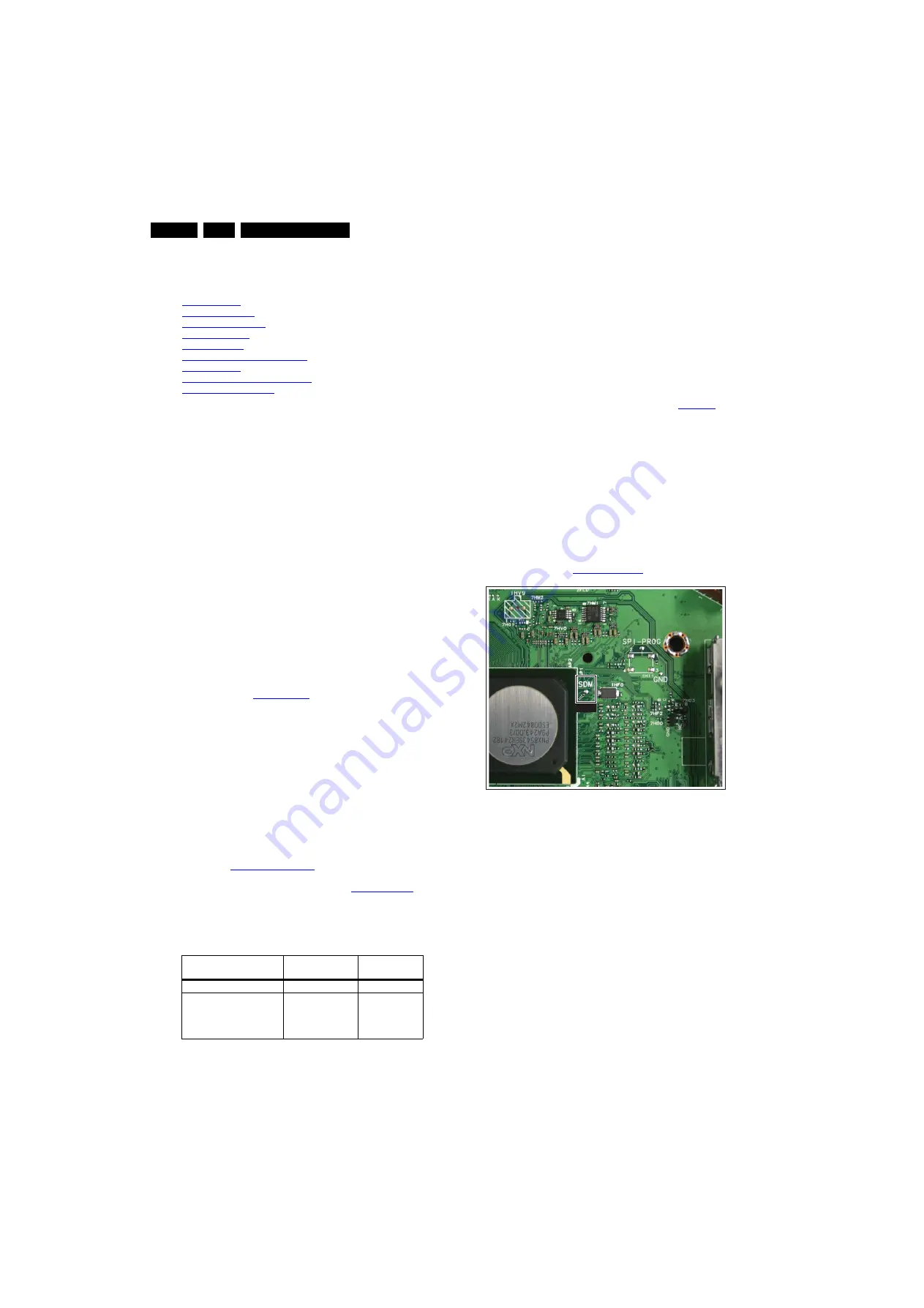
•
Analog
SDM
can also be activated by grounding for a
moment the solder pad on the SSB, with the indication
“SDM” (see figure
).
Figure 5-1 Service mode pad
After activating this mode, “SDM” will appear in the upper right
corner of the screen (when a picture is available).
How to Navigate
When the “MENU” (or HOME) button is pressed on the RC
transmitter, the TV set will toggle between the SDM and the
normal user menu.
How to Exit SDM
Use one of the following methods:
•
Switch the set to STAND-BY via the RC-transmitter.
•
Via a standard customer RC-transmitter: key in “00”-
sequence.
5.2.2
Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
Purpose
•
To perform (software) alignments.
•
To change option settings.
•
To easily identify the used software version.
Region
Freq. (MHz)
Default
system
Europe, AP(PAL/Multi)
475.25
PAL B/G
Europe, AP DVB-T
546.00 PID
Video: 0B 06 PID
PCR: 0B 06 PID
Audio: 0B 07
DVB-T
1
83
10_219_090
3
1
8
.ep
s
090
3
19
S
DM















































