Great user manuals database on
17
Additional Information
P o w e r s a v i n g f e a t u r e / G l o s s a r y
Glos
Glos
s
s
ar
ar
y
y
Here are a few definitions that may help you.
Brightness
Refers to how light or dark the overall screen is.
Color
A term used to refer to the color balance, uniformity, and saturation settings on your monitor screen. Color (even white,
Temperature
gray, and black) on your screen is achieved by blending (or balancing) three primary colors: red, green, and blue. As you
increase or decrease any one of these colors, the color temperature changes. For example, at 9300˚ K, you are using more
blue in your color temperature; therefore, your screen will be saturated with more blue and should appear uniformly “bluer”
from one side of the screen to the other. At 6500˚ K, you are using more red in your mixture. True color balance is achieved
when a gray object shows no traces of either red, green, or blue, regardless of the brightness of the image.
Contrast
Refers to the sharpness of objects on the screen and the ability to easily distinguish one from the other.
Degauss
The process by which metal parts of the screen are demagnetized in order to reduce screen distortion and color impurity.
DDC
(Display Data Channel) is a signaling standard established to help the performance of personal computers. In order to
use this function, your computer must be designed for DDC. There are several types of DDC. Most computer monitors
are designed for DDC1 and DDC2 Level B (DDC1 /2B).
Geometry
A set of controls that allows you to adjust the alignment of the picture on the monitor screen. The goal is to “square up”
the picture. This is done by adjusting such items as balanced pincushion, pincushion, parallelogram, rotation, and
trapezoid.
Moire
A fringe pattern caused by the interference between two superimposed line patterns.
Noise
Term used to refer to interference with the monitor’s picture.
USB
Universal Serial Bus. A way to connect your IBM-compatible computer, monitor, and peripherals for true Plug-and-Play
functions. This is an emerging technology.
A
A
utoma
utoma
tic Power Sa
tic Power Sa
vings &
vings &
Preset R
Preset R
esol
esol
ution Modes
ution Modes
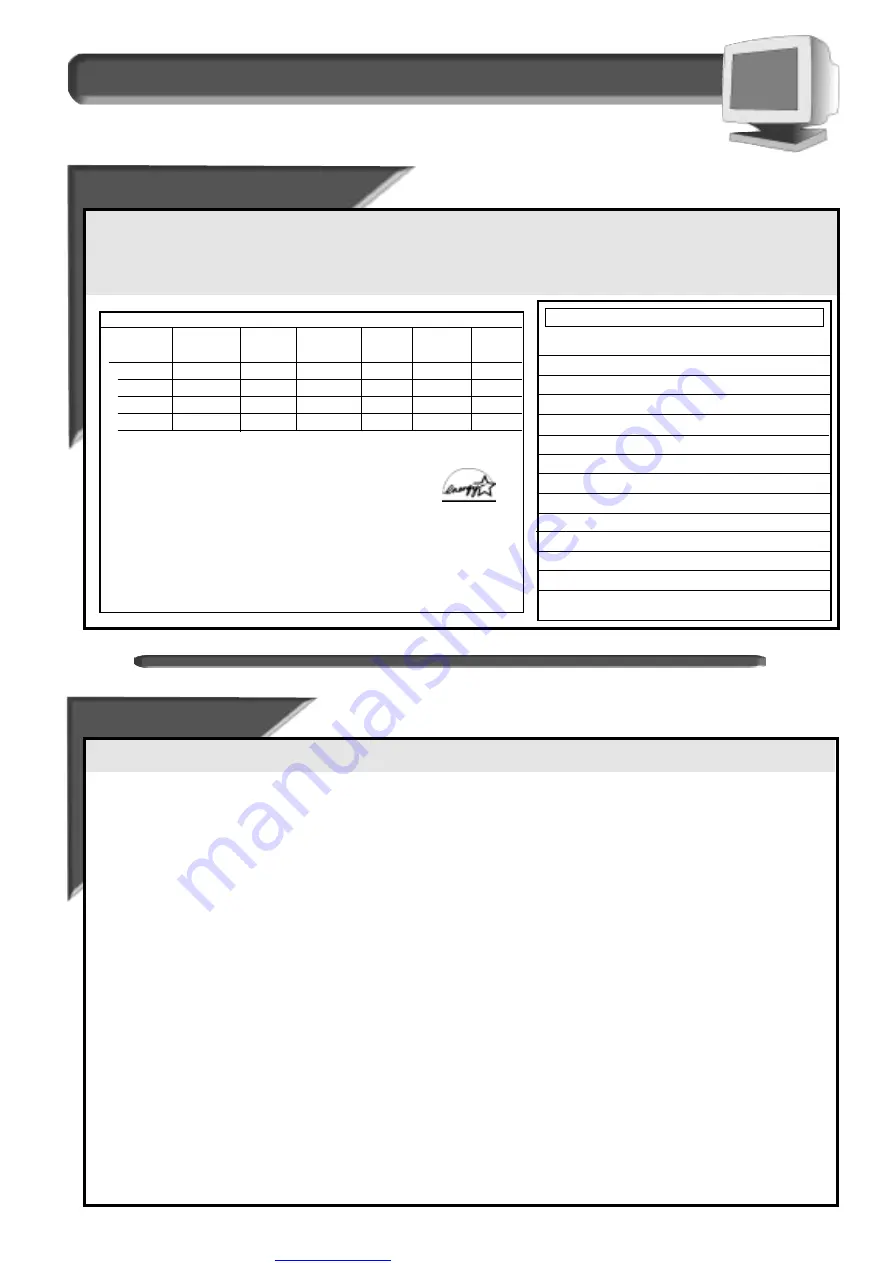
If you have VESA's DPMS compliance display card or software installed in your PC, the monitor can automatically reduce its power consumption when
not in use. If input from a keyboard, mouse, or other device is detected, the monitor automatically “wakes up.” The table at left shows the power
consumption and signalling of this automatic power-saving feature. To turn this feature on and off, see page 7. The table at right shows the 8 factory
preset resolution modes. The maximum number of modes is 12 This leaves room for additions.
Power Management Definition
VESA's mode
Video
H-sync
V-sync
Power Power
LED
used saving(%)
color
ON
Active
Yes
Yes
< 100W
0%
Green
Stand-by
Blanked
No
Yes
< 15W
86%
Yellow
Suspend
Blanked
Yes
No
< 15W
86%
Yellow
OFF
Blanked
No
No
< 5W
95%
Amber
This monitor is Energy Star compliant and power management compatible.
AS AN ENERGY STAR PARTNER, PHILIPS HAS DETERMINED THAT THIS
PRODUCT MEETS THE ENERGY STAR GUIDELINES FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY.
The proper operation of the function requires a computer with VESA DPMS
power management capabilities. When used with a computer equipped with
VESA DPMS, the monitor is Energy Star compliant.
M
ODE
R
ESOLUTION
H. F
REQ
.
V. F
REQ
.
S
TANDARD
(K
HZ
)
(H
Z
)
1
640 x 400
31.5
70
VGA
2
640 x 480
31.5
60
VGA
3
640 x 480
43.3
85
VESA/85
4
800 x 600
46.9
75
VESA/75
5
800 x 600
53.7
85
VESA/85
6
1024 x 768
60
75
VESA/75
7
1024 x 768
68.7
85
VESA/85
8
1280 x 1024
64
60
VESA/60
Factory Preset Resolution Modes
17



































