IG-267-EN versión 01; 07/04/2017
65
General Instructions
ekor
.rpa
Protection, metering and control models
4.
Connect the trip indication signal (depending on the
programmed function) to the tester's timer stop input.
5.
Inject the test currents, additionally secondary circuit
voltage, in order to test the directional or voltage units
and ensure that the switch opens and the tripping
times are correct.
6.
Trip tests must be performed for all toroidal-core
current transformers to check the proper operation of
the complete unit.
1. For phase trip tests, the test cable must be connected
to the test flat bars of two toroidal-core current
transformers. Current therefore passes through
them in contrary direction and neutral current is
not generated. In the case of neutral trips, the test
cable is connected to a single toroidal-core current
transformer (zero-sequence or phase, depending on
whether a zero-sequence transformer is available or
not).
2. Injecting through these test flatbars means the
current flow direction is opposite to that of an
output cubicle; this must be taken into account
when carrying out tests involving current direction.
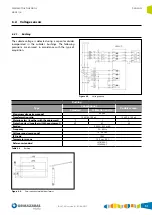
Check by secondary
The current and voltage injection tests for checks by
secondary are carried out through the test terminals enabled
for this purpose. These terminals allow the unit's sensors to
be disconnected, leaving the sensor circuits closed and the
unit inputs open in order to connect the test kit.
Important:
correct connection between sensors and
relay must be ensured once the tests have concluded.
Check by secondary with circuit-breaker operation
In this case, the tests are performed on the equipment
when the cable compartment is not accessible. This occurs
because the cubicle outgoing cables are energised and
cannot be connected to earth. In this case, the test cable
cannot be connected to the test connection in the toroidal-
core current transformers and the current injection is
performed through the test terminal block.
This testing method is also used when the primary circuit
current values being tested are much greater than those
produced by test equipment (normally greater than 100 A),
and in consequence the tests cannot be carried out from
primary.
1.
To perform this check, follow the steps indicated below:
2.
Access the driving mechanism upper compartment,
where the checks and tests terminal block is located.
3.
Short-circuit, and then disconnect the voltage and
current circuit terminals. This procedure short-circuits
the current transformer secondary circuits and branches
the voltage sensor signal to earth.
4.
Connect the test cable to the terminals, taking into
account the differentiation between current and
voltage circuits, and the channel through which it is to
be injected.
5.
Connect the test cable to the current and/or voltage
circuit of the tester.
6.
Connect the trip indication output (depending on the
programmed functionality) to the tester’s timing stop
input.
7.
If the circuit-breaker can be opened, put it in closed
position. If the circuit-breaker cannot be operated, make
sure the bistable release (BINOX) and the tripping coil
remain disconnected, and start the check as explained
in the following section "Check by secondary without
using the circuit-breaker”.
8.
Inject secondary test voltages and currents, taking into
account the current transformer ratios, and calibrate
voltage injection with the test capacitors.
Check by secondary without circuit-breaker operation
The protection cubicle circuit-breaker often cannot be
operated and therefore the maintenance checks are
performed exclusively on the electronic unit. In these cases,
the following points should be taken into account:
1.
Always disconnect the bistable release and the tripping
coil. This way, the relay can trip without acting upon the
opening mechanism.
2.
Then inject the current according to the section above,
called "Check through secondary with circuit-breaker
operation”.
Содержание ekor.rpa Series
Страница 115: ......