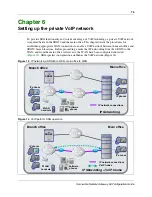
Chapter 6 Setting up the private VoIP network
87
Survivable Remote Gateway 50 Configuration Guide
d
Change the schedule time so that the schedule runs continuously (
Start Time
00:00:00,
Stop Time
23:59:59, MTWTFSS).
e
Change the routing service (
Routing Svc
) to
Auto
.
f
Select
Overflow
.
2
Define a route for calls to the main office over the VoIP trunks and a route to the main office
over the PSTN.
a
Access the
Dialing Plan - Routing
panel (
Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan >
Routing
) and select the
Routes
tab.
b
Add a new route (for example, 998).
c
Ensure that the
DN Type
is
Public (Unknown)
.
d
Assign the VoIP line pool to the route (select the line pool from the
Use Pool
pull-down
menu; default is
BlocA
).
e
Add another new route (for example, 999).
f
Ensure that the
DN Type
is
Public (Unknown)
.
g
In the
External Number
field, enter the
PSTN number
of the main office.
h
Assign the PSTN line pool to the route (select the line pool from the
Use Pool
pull-down
menu; default is
A
).
3
Add a destination code to provide access to the newly created routes. This code is used in both
normal and local modes for dialing the main office from the SRG50 site.
a
Access the
Dialing Plan - Routing
panel (
Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan >
Routing
) and select the
Destination Codes
tab.
b
Add a new destination code (for example,
678
).
c
With the
Destination Code
row highlighted, select the
SRG
schedule from the
Alternate
Routes
list (
Alternate Routes for Destination Code
details panel).
d
In the
First Route
field, enter
998
(the VoIP route).
e
In the adjacent
Absorbed Length
field, select the number of digits to be absorbed. The
Absorbed Length
applies to the digits of the destination code only.
Typically, the
Absorbed Length
is
All
for UDP and
0
for CDP.
f
In the
Second Route
field, enter
999
(the PSTN route).
g
In the adjacent
Absorbed Length
field, select the number of digits to be absorbed.
Depending on the dialing plan, the destination code is integrated with the DN or is dialed as a
prefix to the DN. When a user calls the main office, the SRG50 examines the destination code to
determine the routing. If the
First Route
, the VoIP trunks, is unavailable, the call is routed to the
Second Route
, the PSTN, and the
External Number
is called. Because
Overflow
was selected, if
both the
First Route
and the
Second Route
are unavailable, the call is routed using the
Normal
Route
specified in the
Normal Route
column of the
Destination Codes
table. Because
Auto
was
selected, the routing occurs without manual intervention.
Содержание SRG50
Страница 1: ...Part No N0060720 03 December 2007 Survivable Remote Gateway 50 Configuration Guide...
Страница 4: ...4 Task List N0060720 N0060720 Glossary 107 Index 109...
Страница 8: ...8 Contents N0060720...
Страница 26: ...26 Chapter 1 Getting started N0060720 N0060720...
Страница 50: ...50 Chapter 3 CS 1000 considerations N0060720 N0060720 Figure 6 S1000 IP Terminal Details panel...
Страница 62: ...62 Chapter 4 CS 2000 considerations N0060720 N0060720...
Страница 100: ...100 Chapter 8 Troubleshooting N0060720...
Страница 106: ...106 Telephone features in normal and local mode N0060720...