MOTOROLA
M68000 8-/16-/32-BIT MICROPROCESSORS USER'S MANUAL
5- 23
BUS THREE-STATED
BG ASSERTED
BR VALID INTERNAL
BR SAMPLED
BR ASSERTED
BUS RELEASED FROM THREE STATE AND
PROCESSOR STARTS NEXT BUS CYCLE
BR NEGATED INTERNAL
BR SAMPLED
BR NEGATED
BR
BG
BGACK
AS
UDS
LDS
R/W
DTACK
D15–D0
S0
S2
S4
S6
S0
S2
S4
S6
S0
CLK
FC2–FC0
A23–A1
PROCESSOR
ALTERNATE BUS MASTER
PROCESSOR
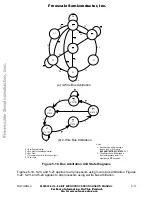
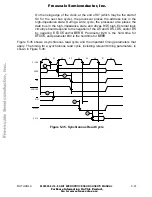
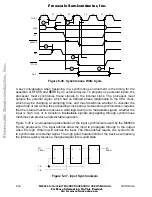
Figure 5-24. 2-Wire Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram—Special Case
5.4. BUS ERROR AND HALT OPERATION
In a bus architecture that requires a handshake from an external device, such as the
asynchronous bus used in the M68000 Family, the handshake may not always occur. A
bus error input is provided to terminate a bus cycle in error when the expected signal is
not asserted. Different systems and different devices within the same system require
different maximum-response times. External circuitry can be provided to assert the bus
error signal after the appropriate delay following the assertion of address strobe.
In a virtual memory system, the bus error signal can be used to indicate either a page fault
or a bus timeout. An external memory management unit asserts bus error when the page
that contains the required data is not resident in memory. The processor suspends
execution of the current instruction while the page is loaded into memory. The MC68010
pushes enough information on the stack to be able to resume execution of the instruction
following return from the bus error exception handler.
F
re
e
sc
a
le
S
e
m
ic
o
n
d
u
c
to
r,
I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
n
c
.
..