Quality Crimp Handbook
Order No 63800-0029
Release Date:09-04-03
UNCONTROLLED COPY
Page 8 of 24
Revision: B
Revision Date: 10-07-05
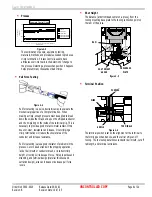
Figure 4-4
28.5
29.5
30.5
31.5
Thousandths
Measurements
Crimp Height
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1011 1213 14 1516 17 18 1920 21 2223 24 25
Sample
Contol Limit
Control Limit
Upper Specification
Lower Specification
Example Control Chart
Figure 4-3
Figure 4-5
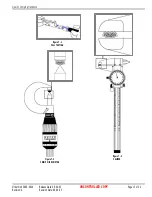
RAM
PRESS BASE
PLATE
SHUT HEIGHT
GAUGE
Figure 4-6
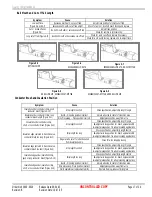
PUNCHES
WIRE
ANVILS
TERMINALS
§
Process
The combination of people, equipment, tooling,
materials, methods, and procedures needed to produce a
crimp termination. Process Control is used to track
attributes over time to aid in the detection of change to
the process. Detecting a process change when it happens
helps prevent many thousands of bad crimps.
§
Pull Force Testing
Pull force testing is a quick, destructive way to evaluate the
mechanical properties of a crimp termination. When
making a crimp, enough pressure must be applied to break
down the oxides that may build up on the stripped conductor
and the tin-plating on the inside of the terminal grip. This is
necessary to provide a good metal-to-metal contact. If this
does not occur, resistance can increase. Over-crimping a
crimp termination will reduce the circular area of the
conductor and increase resistance.
Pull force testing is also a good indicator of problems in the
process. Cut or nicked strands in the stripping operation,
lack of bell mouth or conductor brush, or incorrect crimp
height or tooling will reduce pull force. Wire properties and
stranding, and terminal design (material thickness and
serration design), also can increase or decrease pull force
levels.
§
Shut Height
The distance (at bottom dead center on a press), from the
tooling mounting base plate to the tooling connection point on
the ram of the press.
§
Terminal Position
The terminal position is set by the alignment of the terminal to
the forming punch and anvils, and the carrier strip cut-off
tooling. The tool set-up determines conductor bell mouth, cut-off
tab length, and terminal extrusions.