38
Chapter 6. PID stabilisation
6.4
Noise-eater implementation
A
common
application
for
PID
controllers
is
optical
noise
eating,
which technical noise arising from power fluctuations in a laser beam.
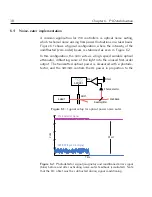
Figure 6.1 shows a typical configuration, where the intensity of the
undiffracted (zero-order) beam is stabilised as seen in Figure 6.2.
In this configuration, the
AOM
acts as a high-speed variable optical
attenuator, diffracting some of the light into the unused first-order
output.
The transmitted optical power is measured with a photode-
tector, and the
ARF/XRF
controls the
RF
power in proportion to the
Photodetector
AOM
Laser
Stabilised
Offset
ARF/XRF
Beamsplitter
+
–
Error
Figure 6.1:
Typical setup for optical power noise eater.
Time
Time
Volts
Offset
Photodetector signal
ARF/XRF input error signal
1
2
3
4
5
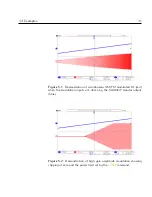
Figure 6.2:
Photodetector signal (magneta) and conditioned error signal
(blue) before and after activating noise-eater feedback (simulated).
Note
that the DC offset must be subtracted during signal conditioning.
Содержание ARF021
Страница 1: ...Agile RF Synthesizer AOM driver ARF021 ARF421 XRF021 XRF421 Version 1 5 0 Rev 6 ...
Страница 4: ...ii ...
Страница 10: ...viii Contents ...
Страница 26: ...16 Chapter 3 Communications ...
Страница 44: ...34 Chapter 5 External modulation ...
Страница 50: ...40 Chapter 6 PID stabilisation ...
Страница 64: ...54 Chapter 7 Digital I O ...
Страница 100: ...90 Chapter 9 Advanced table mode XRF ...
Страница 128: ...118 Appendix C Command language ...
Страница 133: ......