10
ACRYLAMIDE IN FOODSTUFFS
Which foods are affected?
Acrylamide is mainly produced in grain and potato products that
are heated to high temperatures, such as potato crisps, chips, toast,
bread rolls, bread, fine baked goods (biscuits, gingerbread, cookies).
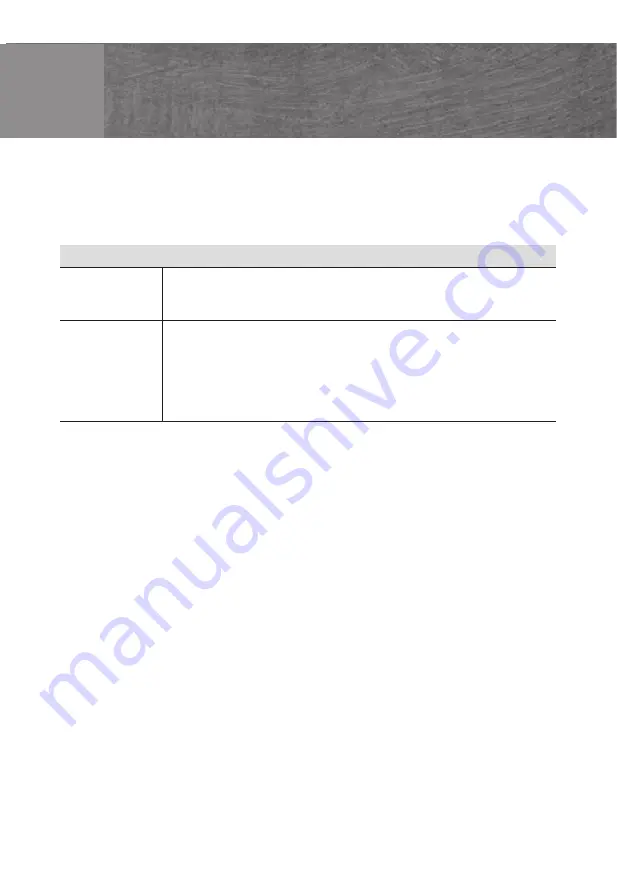
Tips for keeping acrylamide to a minimum when preparing food
General
Baking biscuits
Oven chips
Keep cooking times to a minimum. Cook meals until they are
golden brown, but not too dark. Large, thick pieces of food
contain less acrylamide.
Max. 200 °C in Top/bottom heating or max. 180 °C in 3D hot air
or hot air mode. Max. 190° C in Top/bottom heating or max.
170 °C in 3D hot air or hot air mode. Egg white and egg yolk
reduce the formation of acrylamide. Distribute thinly and evenly
over the baking tray. Cook at least 400 g at once on a baking
tray so that the chips do not dry out.
EN-30