www.megger.com
35
General Information
Ground resistance testing – Basic principles
Principle of operation (three-terminal resistance measurement)
The classic “fall of potential” test is used to accurately measure the resistance of an Ground electrode using
auxiliary stakes driven into the soil, which form a circuit for the test current injection and voltage measurement
as used for the two-terminal method.
The MFT injects AC of known magnitude into the system under test and measures the voltage developed across
it as shown below. The system resistance is a simple ratio as per ohm’s Law. In this case, the potential stake is
moved by fixed increments in a straight line between the electrode under test and the current stake. At each
location, the resistance is calculated as R=V/I. A graph of resistance versus potential stake position is plotted
and the resistance of the electrode under test is taken to be the point at which the curve is flattest.
Empirical testing has shown that with suitably positioned stakes, this method can be shortened by placing the
potential stake at a distance of approximately 62% between the electrode under test and the current stake, i.e.
at A = 0.62 x B.
Earth electrode
under test
C (H)
P (S)
X (E)
V
I
Potential stake
Current stake
A
B
Schematic for three-terminal resistance measurement
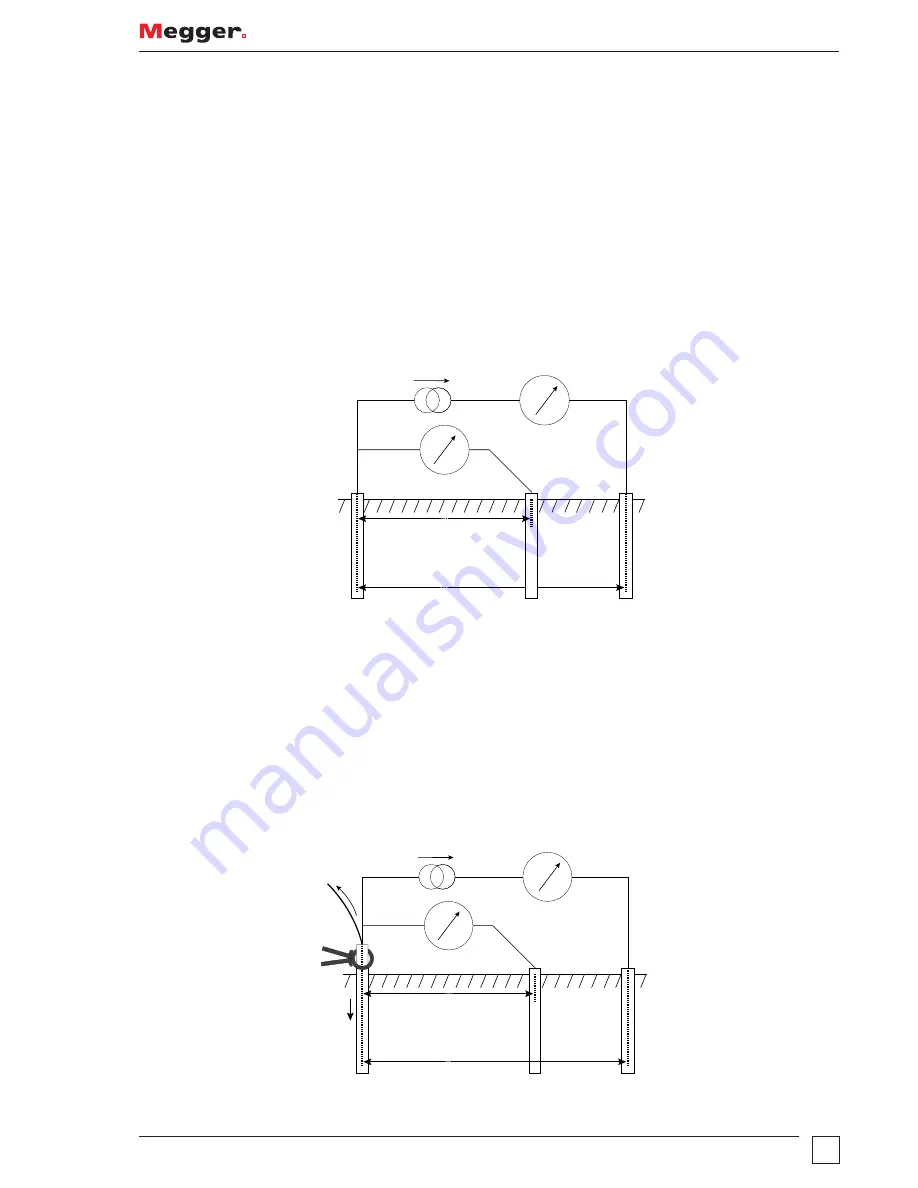
Principle of operation (three-terminal resistance measurement using ART)
The classic three-terminal test method has a disadvantage, namely that the electrode under test must be
disconnected from the system it is supposed to protect in the event of a power system fault. The reason for
this is that the injected test current will take all possible routes to ground and not all of it will necessarily flow
through the electrode under test. In this case, the instrument will make a reading of the entire grounding
network, not just the individual electrode.
By using a current transducer (the Megger Megger Current Clamp) to measure the current flowing through the
electrode under test as a fraction of the total test current injected, the instrument can determine the individual
resistance. This arrangement is shown below:
A
Earth electrode
under test
Connection
to rest of system
B
C (H)
P (S)
X (E)
I2
I1
Potential stake
ICLAMP
Current stake
V
I
Schematic for three-terminal resistance measurement using an IClamp






































