Page 11
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
ÉÉÉÉÉÉÉÉ
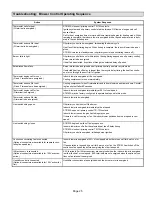
A
1" (25 mm)
min
A
Figure 11
combustible
material
Radiation Shield Installation
SLO183B
unit
(top)
SLO183B
unit
(front)
radiation
shields
flue
pipe
B
unit
cabinet
NOTE 1−Radiation shields must be constructed of 24 gauge sheet
metal
minimum
.
NOTE 2−Radiation shields required when A is less than 9" (229 mm).
NOTE 3−Radiation shields should extend from the top of the unit to
the top of the flue pipe.
noncombustible
spacers
radiation shields
(see note 1)
12" (305 mm)
min
7" (178 mm)
min
see note 2
see note 3
Barometric Draft Control Installation
Install the provided barometric draft control in the flue pipe
at least 12 inches
beyond the furnace flue outlet to provide
space for flue gas sampling. The barometric draft control
may be installed in either vertical or horizontal sections of
the flue pipe; however, it should be positioned
no more
than 18"
beyond the furnace flue outlet. Follow the instruc-
tions packed with the barometric draft control.
Alternate Side Flue Connections
The vent pipe may exit the top or sides of the cabinet. A
hole is provided in the top cap for top exit. For side exit, lo-
cate the center hole punched in the side of the cabinet. See
unit dimensions on page 2. Using it as the center point, cut
a 6 inch (152 mm) round hole in the cabinet’s side. Install
the barometric draft control within 18 inches of the furnace
flue outlet. Attach the provided finishing plate to cover
rough edges.
Supply & Return Air Plenums
Secure return air plenum to unit using sheet metal screws.
NOTE − The following are suggested procedures that
should be followed when installing the supply air plenum.
1 − Use sealing strips of fiberglass.
2 − In all cases, the plenum should be secured to furnace
or evaporator cabinet with sheet metal screws.
3 − Install supply and return air ducts as desired.
Oil Supply Line Sizing
Ensure that the restrictions of the piping system, plus any
lift involved, do not exceed the capability of the oil pump.
Use the following guidelines and table 5 when determining
whether to use a single−or two−stage oil pump.
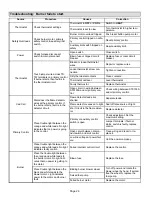
One−Pipe System
When using a one−pipe system with the oil tank above the
burner, or a one−pipe system with no more than an 8−ft.
(2.4m) lift and a vacuum of 6" (152 mm) Hg or less, a single−
stage fuel pump with a supply line should be adequate with-
out a separate return line. See figure 12. Manual bleeding
of the fuel pump is required on initial start up. Failure to
bleed air from the oil pump could result in an air lock/oil
starvation condition.
NOTE − As an extra precaution, cycle heating on and off ten
times after bleeding air from the oil pump. This will elimi-
nate air in the gun assembly.
To determine pipe sizing for a one−pipe application, refer to
table 3.
Figure 12
Oil Piping
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
ÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎÎ
Air Vent
Fill
Pipe
Oil
Tank
Fuel
Pump
Aux
Filter
Shut−Off
Valve
8 ft (2.4 m)
Maximum
Lift
One-Pipe System
Table 3
One−Pipe Oil Line Sizing
Line Length
Pipe Diameter (OD Tubing)
0−50’ (15 m)
3/8" (10 mm)
51−100’ (15 m)
1/2" (12 mm)
Two−Pipe System
When using a two−pipe system with the oil tank below the
level of the burner, a single−stage fuel pump should be used
in lift conditions of up to 10 feet (3 m) and/or a vacuum of
12" Hg or less. See figure 13. Use a two−stage fuel pump
when lift exceeds 10 feet (3 m) and/or the vacuum is in the
range of 12" Hg to 17" Hg.