28
14.3.3 Gas Tightness Test
To prevent faults caused by refrigerant leakage, a gas
tightness test should be performed before system
commissioning.
● Only dry nitrogen should be used for gas
tightness testing. Oxygen, air, flammable
gases and toxic gases must not be used for
gas tightness testing. Use of such gases may
result in fire or explosion.
● Make sure that all the outdoor unit stop valves
are firmly closed.
● Make sure all piping connections are complete
before the tightness test begins.
CAUTION
The gas tightness test procedure is as follows:
1.Charge the indoor piping with nitrogen at 0.3Mpa
through the needle valves on the liquid and gas stop
valves and leave for at least 3 minutes (do not open the
liquid or gas stop valves). Observe the pressure gauge to
check for large leakages. If there is a large leakage, the
pressure gauge will drop quickly.
2.If there are no large leakages, charge the piping with
nitrogen at 1.5Mpa and leave for at least 3 minutes.
Observe the pressure gauge to check for small leakages.
If there is a small leakage, the pressure gauge will drop
distinctly.
3.If there are no small leakages, charge the piping with
nitrogen at 4.2 MPa and leave for at least 24 hours to
check for micro leakages. Micro leakages are difficult
to detect. To check for micro leakages, allow for any
change in ambient temperature over the test period by
adjusting the reference pressure by 0.01Mpa per 1°C of
temperature difference. Adjusted reference pressure =
Pressure at pressuri (temperature at observation
– temperature at pressurization) x 0.01Mpa. Compare
the observed pressure with the adjusted reference
pressure. If they are the same, the piping has passed
the gas tightness test. If the observed pressure is lower
than the adjusted reference pressure, the piping has a
micro leakage.
4.If the leakage is detected, refer to following part “Leak
detection”. Once the leak has been found and fixed, the
gas tightness test should be repeated.
5.If not continuing straight to vacuum drying once
the gas tightness test is complete, reduce the
system pressure to 0.5-0.8MPa and leave the system
pressurized until ready to carry out the vacuum drying
procedure.
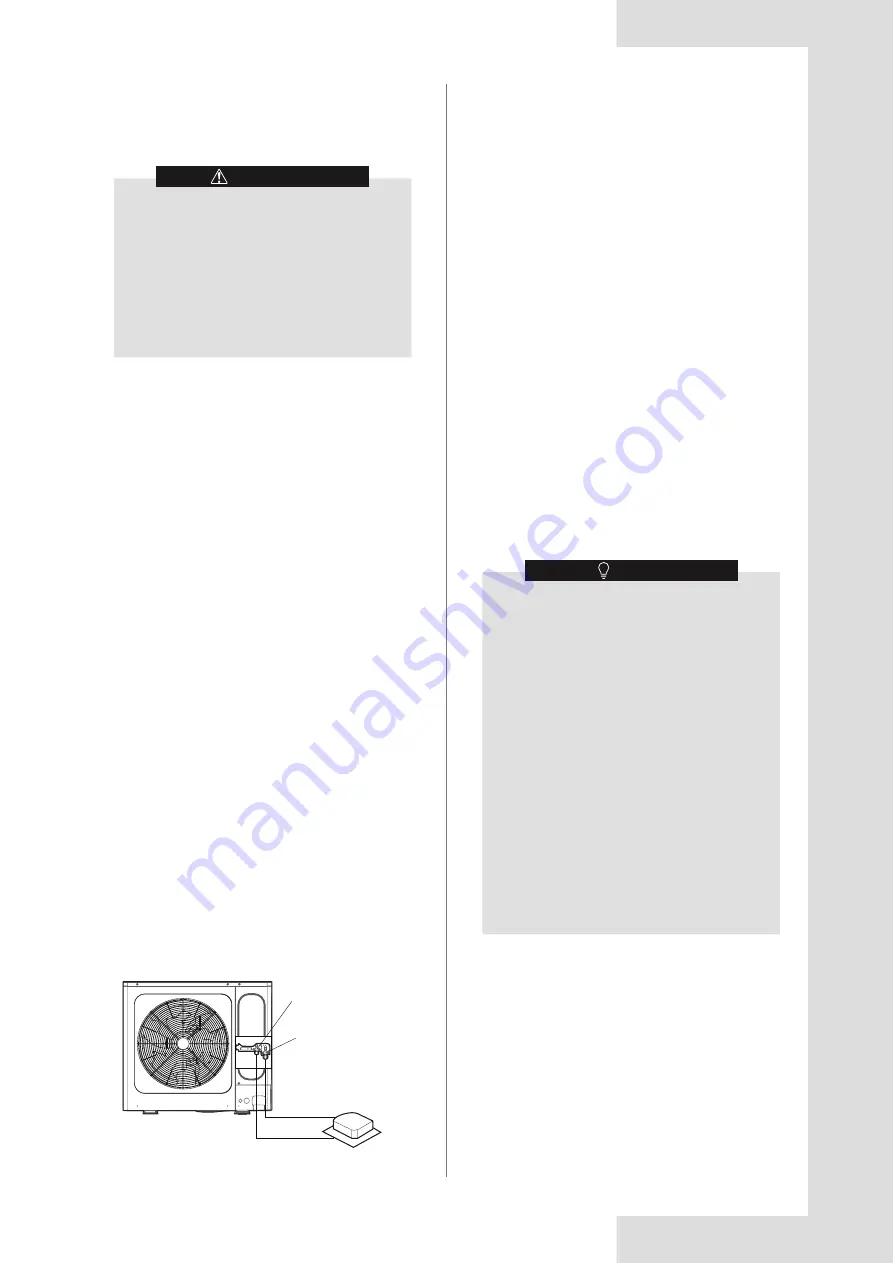
Gas side of
stop valve
Liquid side of
stop valve
Gas pipe
Liquid pipe
Indoor unit
Outdoor unit
Figure 14-16
14.3.4 Leak Test
The general methods for identifying the source of a leak
are as follows:
1. Audio detection: relatively large leaks are audible.
2. Touch detection: place your hand at joints to feel for
escaping gas.
3. Soapy water detection: small leaks can be detected
by the formation of bubbles when soapy water is applied
to a joint.
4.Electronic leak detector detection: electronic leak
detector shall be used to check whether air leaks at each
joint.
14.3.5 Vacuum Drying
Vacuum drying should be performed in order to remove
moisture and non-condensable gases from the system.
Removing moisture prevents ice formation and oxidization
of copper piping or other internal components. The
presence of ice particles in the system would cause
abnormal operation, whilst particles of oxidized copper
can cause compressor damage. The presence of non-
condensable gases in the system would lead to pressure
fluctuations and poor heat exchange performance.
Vacuum drying also provides additional leak detection (in
addition to the gas tightness test).
● Before performing vacuum drying, make sure
that all the outdoor unit stop valves are firmly
closed.
● Once the vacuum drying is complete and the
vacuum pump is stopped, the low pressure in
the piping could suck vacuum pump lubricant
into the air conditioning system. The same
could happen if the vacuum pump stops
unexpectedly during the vacuum drying
procedure. Mixing of pump lubricant with
compressor oil could cause compressor
malfunction. Therefore, a check valve should
be used to prevent vacuum pump lubricant
seeping into the piping system.
● Vacuumize using a vacuum pump. Do not use
refrigerant gas to discharge air.
● To prevent the entry of impurities, the R32
special tool must be used to ensure compression
strength is maintained. Use a charging hose
with a top rod to connect to the access hole of
the stop valve or the refrigerant charging port.
NOTE
Содержание KMF-80 DVR5
Страница 67: ...16127000005207...
Страница 68: ......
















































