Table 64: Resolution of Indirect Next Hops
(continued)
Table in Which BGP Indirect Next Hop Resolves
Route Type
IP tunnel routing table
Labeled VPN
BGP Advertising Rules for Labeled and Unlabeled Routes with the Same AFI
When BGP receives a route to a prefix with the same AFI in both labeled and unlabeled
forms, only one of these routes can be selected as the best route. The action taken
after the best route is selected depends on whether the best route is labeled or
unlabeled, and on what SAFI was previously negotiated with peers other than the
one from which it received the best route. Table 65 on page 461 lists the advertising
action taken for the best route, whether labeled or unlabeled.
Table 65: Advertising Action Taken Following Best Route Selection
Action Taken
SAFI Negotiated with Peer
Best Route
Advertises unlabeled route.
SAFI 1 and SAFI 4 (unlabeled
and labeled)
Unlabeled
Advertises unlabeled route.
SAFI 1 (unlabeled)
Unlabeled
Withdraws labeled route.
SAFI 4 (labeled)
Unlabeled
Advertises labeled route.
SAFI 1 and SAFI 4 (unlabeled
and labeled)
Labeled
Withdraws unlabeled route.
SAFI 1 (unlabeled)
Labeled
Advertises labeled route.
SAFI 4 (labeled)
Labeled
BGP sends a route-refresh message for each SAFI that it has negotiated with a peer.
For example, if a speaker has negotiated both SAFI 1 and SAFI 4 with a particular
peer, then when you issue the
clear ip bgp neighbor soft-in
command, BGP sends
two route-refresh messages to this neighbor, one for each SAFI.
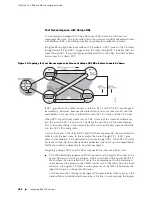
Providing Internet Access to and from VPNs
Normally, hosts in a VPN cannot communicate with hosts in the Internet because
the routing table in a VRF contains only routes to sites in the VPN and not routes to
sites in the Internet. The exchange of traffic between a VPN and the Internet requires
both of the following:
■
Traffic flow from the VPN to the Internet
■
Traffic flow from the Internet to the VPN
The most common, and simplest, method for providing Internet access is to configure
two separate logical circuits. One logical circuit runs between the CE router and the
Providing Internet Access to and from VPNs
■
461
Chapter 5: Configuring BGP-MPLS Applications
Содержание BGP
Страница 6: ...vi ...
Страница 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 37: ...Part 1 Border Gateway Protocol Configuring BGP Routing on page 3 Border Gateway Protocol 1 ...
Страница 38: ...2 Border Gateway Protocol JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 234: ...198 Monitoring BGP JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 236: ...200 Multiprotocol Layer Switching JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 350: ...314 Example Traffic Class Configuration for Differentiated Services JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 541: ... There is no no version See undebug ip mbgp Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs 505 Chapter 5 Configuring BGP MPLS Applications ...
Страница 542: ...506 Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 544: ...508 Layer 2 Services Over MPLS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 598: ...562 Multiple ATM Virtual Circuits over a Single Pseudowire Example JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 610: ...574 Virtual Private LAN Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 624: ...588 VPLS References JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 648: ...612 VPLS Configuration Example with LDP Signaling JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 680: ...644 Virtual Private Wire Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 724: ...688 Monitoring MPLS Forwarding Table for VPWS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 725: ...Part 6 Index Index on page 691 Index 689 ...
Страница 726: ...690 Index JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...