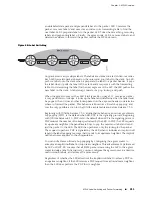
Table 23: MPLS Terms and Acronyms
(continued)
Definition
Term
Label-only-inferred-PSC LSP. The label value, and possibly the
EXP-bits, are used to determine the per-hop behavior applied to the
packet.
L-LSP
Label-switching router—An MPLS node that can forward layer 3
packets based on their labels
LSR
Multiprotocol Label Switching—Set of techniques enabling forwarding
of traffic using layer 2 and layer 3 information
MPLS
MPLS node that connects an MPLS domain with a node outside the
domain that either does not run MPLS or is in a different domain
MPLS edge node
MPLS edge node in the role of handling traffic as it leaves an MPLS
domain
MPLS egress node
MPLS edge node in the role of handling traffic as it enters an MPLS
domain
MPLS ingress node
Label carried in a packet header that represents a packet’s
forwarding equivalence class
MPLS label
A router running MPLS. An MPLS node is aware of MPLS control
protocols, operates one or more L3 routing protocols, and is capable
of forwarding packets based on labels. Optionally, an MPLS node
can be capable of forwarding native L3 packets.
MPLS node
The series of LSRs and links that form the path from an ingress LSR
to all of its egress LSRs. Each tunnel is uniquely identified by a
session object.
Point-to-multipoint tunnel
An RSVP-TE LSP with a single ingress LSR and one or more egress
LSRs. Incoming data is replicated at the branch nodes.
Point-to-multipoint LSP
PE—An LER at the edge of a service provider core that provides
ingress to or egress from a VPN
Provider edge router
P—An LSR within a service provider core that carries traffic for a
VPN
Provider core router
Resource Reservation Protocol; E Series routers do not support RSVP
RSVP
Resource Reservation Protocol enhanced to support MPLS traffic
engineering; E Series routers support RSVP-TE
RSVP-TE
The portion of the LSP from one LSR to another LSR in a
point-to-multipoint tunnel.
Sub-LSP
The ability to control the path taken through a network or portion
of a network based on a set of traffic parameters (bandwidth, QoS
parameters, and so on). Traffic engineering (TE) enables
performance optimization of operational networks and their
resources.
Traffic engineering
MPLS Terms and Acronyms
■
205
Chapter 2: MPLS Overview
Содержание BGP
Страница 6: ...vi ...
Страница 8: ...viii JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 37: ...Part 1 Border Gateway Protocol Configuring BGP Routing on page 3 Border Gateway Protocol 1 ...
Страница 38: ...2 Border Gateway Protocol JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 234: ...198 Monitoring BGP JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 236: ...200 Multiprotocol Layer Switching JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 350: ...314 Example Traffic Class Configuration for Differentiated Services JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 541: ... There is no no version See undebug ip mbgp Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs 505 Chapter 5 Configuring BGP MPLS Applications ...
Страница 542: ...506 Monitoring BGP MPLS VPNs JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 544: ...508 Layer 2 Services Over MPLS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 598: ...562 Multiple ATM Virtual Circuits over a Single Pseudowire Example JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 610: ...574 Virtual Private LAN Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 624: ...588 VPLS References JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 648: ...612 VPLS Configuration Example with LDP Signaling JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 680: ...644 Virtual Private Wire Service JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 724: ...688 Monitoring MPLS Forwarding Table for VPWS JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...
Страница 725: ...Part 6 Index Index on page 691 Index 689 ...
Страница 726: ...690 Index JUNOSe 11 1 x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide ...