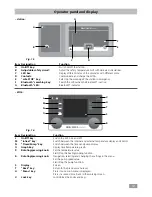
18
• Menu (Details):
TEMPERING:
Control:
Control Mode:
Internal (int):
The temperature is regulated according to
the internal temperature sensor�
Extern (ext):
The temperature is regulated according to
the external temperature sensor�
Control parameters:
Automatic:
The optimal control parameters for PID tem-
perature control are determined automatically� This is the
recommended mode�
Selecting "Automatic" allows you to set the dynamics for
temperature control�
Accurate:
precise tempering without overshooting�
Fast:
fast tempering with minimal overshooting�
Ts
must be adjusted to match the response characteristic
(total of all time constants) of the closed loop controlled
system, so that the control variable can deliver a uniform
and measurable change in the control deviation�
Ts
val-
ues that are too small or too large can lead to instability
of the controller�
Prop_Bp:
Proportional Band Maximum�
Prop_Bn:
Proportional Band Minimum�
The Proportional Band is the range below (Prop_Bp) and
above (Prop_Bn) the set value in which the control output
value is calculated via the difference between the actual
and the set value and the PID parameters�
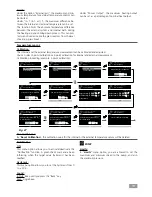
Examples of non-optimal settings:
°C
t
Fig. 25
Manual:
The control parameters for PID temperature con-
trol can be set manually�
"Manual" should only be used in the event of special tem-
perature control requirements�
When "Manual" is selected, the following parameters can
be set for "Internal (int)" and "External (ext)" temperature
control:
Kp:
Proportional coefficient
The proportional coefficient
Kp
is the controller amplifi-
cation and determines how strongly the control deviation
(the difference between the target temperature and ac-
tual temperature) directly affects the control variable (on-
time of the cooling)�
Kp
-values that are too large can lead
to the controller overshooting�
Ti:
Integral time
The integral time
Ti
(s) is the correction time and deter-
mines how strongly the duration of the control deviation
affects the control variable�
Ti
compensates for an ex-
isting control deviation� A high
Ti
means a smaller and
slower effect on the control variable�
Ti
-values that are
too small can lead to instability of the controller�
Td:
Differential time
The differential time
Td
(s) is the derivative time and de-
termines how strongly the rate of change of the control
deviation affects the control variable�
Td
compensates for
rapid control deviations� A high
Td
means a smaller and
slower effect on the control variable�
Td
-values that are
too large can lead to instability of the controller�
Ts:
Sampling time
The sampling time
Ts
(s) is the time interval over which the
control deviation is determined and the respective control
variable (dependent on
Kp
,
Ti
and
Td
) is calculated�
Fig. 26
°C
t
Kp too high
°C
t
Ti too low
°C
t
Td too high
°C
t
Kp too low
Ti too high
Fluids:
Under the option "Fluids", a variety of fluids can be se-
lected�
The selected fluid limits the setting range of the target
temperature� See table in the section “Fluid (Standard in-
formation for
IKA
®
fluid)“�
The maximum and minimum temperature values of the
selected fluid can be set within these limitations�
Cooling:
This menu option allows you to activate/deactivate the
Cooling function�
(heating curve in "Automatic" mode)