HRW HPE-BNMBUS V401 Manual 180307 E. & O. E. / Subject to change without notice
Page 8 of 24
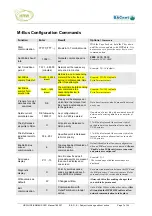
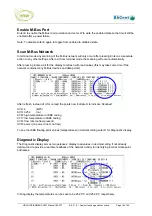
M-Bus Reading Structure
Data point search
When an M-Bus device responds to a read request it will provide the data as a series of Response
(RSP) pages. These may be anything from one page to many pages, depending on the number of data
points available from the meter.
To make best use of the available gateway points the gateway will only extract from these pages the
data points that you configure.
Because M-Bus protocol does not enable the gateway to request a specific page or data point then it is
important that the points you require are configured in the gateway in the same sequence as they
appear in the M-Bus device manufacturer’s RSP page/table sequence, otherwise the gateway may
spend unnecessary time searching for data points that have previously been passed in the RSP page
sequence.
Data point address
Each data point in the device pages consists of DIF (Data Information Field) which indicates the data
type (DEC, HEX, BIN, number of data bytes) and one of more VIF (Variable Information Field) which
indicate information such as decimal placement.
In the gateway the DIF must be specified, as minimum criteria, to identify the data point required to be
read. The VIF’s (up to two) may also need to be specified additionally where an identical DIF is used for
more than one data point. This need of VIF definition is particularly true where two data points have
identical DIF value but it is only the subsequent of the two data points having identical DIF that you
want to read.
If both points with identical DIF are required for reading then only the DIF need be defined for both
because the gateway will find the first based on the DIF value and then find the next with same DIF
value as it moves on to search the remaining page records.
When all required points are found the search will end and the gateway will move on to requesting the
next network meter address point in it’s configured point data base