7
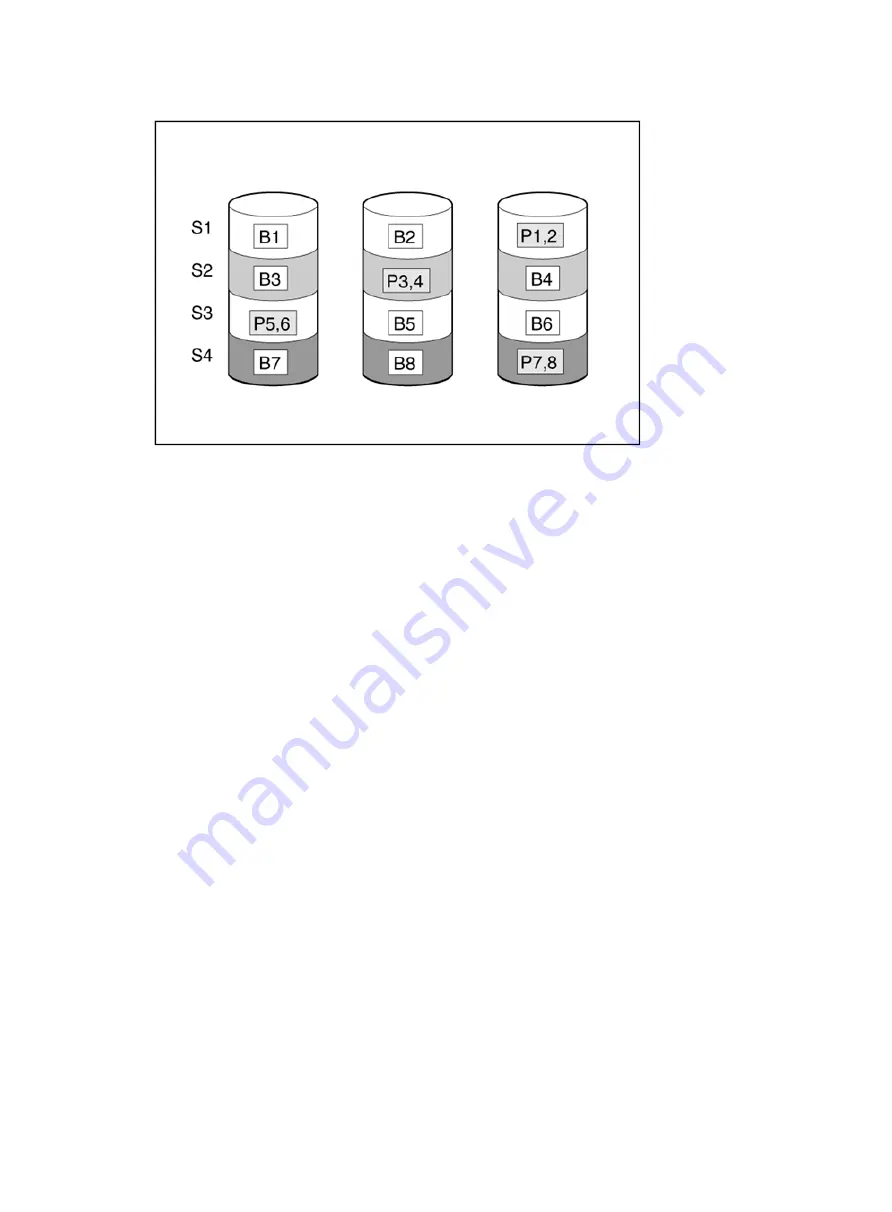
Figure 8 RAID 5
When a physical drive fails, data that was on the failed drive can be calculated from the remaining
parity data and user data on the other drives in the array. This recovered data is usually written to
an online spare in a process called a rebuild.
Application scenarios
RAID 5 is useful when cost, performance, and data availability are equally important.
Advantages
•
Has high read performance.
•
Data is not lost if only one physical drive fails.
•
More drive capacity is usable than with RAID 10, because parity information requires only the
storage space equivalent to one physical drive.
Disadvantages
•
Has relatively low write performance.
•
Data is lost if a second drive fails before data from the first failed drive is rebuilt.
RAID 6
As shown in
, RAID 6, like RAID 5, generates and stores parity information to protect
against data loss caused by drive failure. However, RAID 6 uses two different sets of parity data
(denoted by P
x,y
and Q
x,y
), allowing data to still be preserved if two drives fail. Each set of parity data
uses a capacity equivalent to that of one of the constituent drives.
Содержание UniServer R4300 G6
Страница 36: ...21 Figure 23 Selecting the controller and RAID level 4 Select drives and then click Next...
Страница 40: ...25 Figure 27 Selecting the RAID array to be deleted 2 In the dialog box that opens click Yes...
Страница 41: ...26 Figure 28 Confirming the deletion 3 Verify that the RAID array has been deleted on the Volumes page...
Страница 65: ...23 Figure 36 Modifying RAID parameters 6 Confirm the RAID volume information and then click Create Volume...
Страница 66: ...24 Figure 37 Confirming RAID creation 7 Click OK to complete the RAID creation...
Страница 70: ...28 Figure 41 Setting the selected drive as a hot spare drive 4 In the dialog box that opens click Yes...
Страница 73: ...31 Figure 44 Deleting a RAID array 3 In the dialog box that opens click Yes as shown in Figure 45...
Страница 164: ...89 Figure 158 Selecting Main Menu 2 Select Controller Management and press Enter...
Страница 301: ...70 Figure 116 Array Configuration screen 3 On the screen as shown in Figure 117 select the target array and press Enter...
Страница 312: ...81 Figure 129 Erasing a drive 3 On the screen as shown in Figure 130 select the erase pattern and press Enter...
Страница 321: ...90 Figure 138 Configure Controller Settings screen for the RAID P460 B2...
Страница 330: ...99 Figure 147 Manage Arrays screen 5 On the screen as shown in Figure 148 select Create Logical Drive...
Страница 469: ...19 Examples Viewing physical drive informatoin Syntax mnv_cli info o pd Examples...
Страница 512: ...6 2 Select Main Menu and then press Enter Figure 9 Selecting Main Menu 3 Select Drive Management and then press Enter...
Страница 513: ...7 Figure 10 Selecting Drive Management 4 Select the target drive and then press Enter...
Страница 514: ...8 Figure 11 Select the target drive 5 View the value of the Status field...
Страница 521: ...15 Figure 22 Selecting the storage controller 2 Select Main Menu and then press Enter Figure 23 Selecting Main Menu...
Страница 529: ...23 Figure 33 Identifying a storage controller 2...






































