415
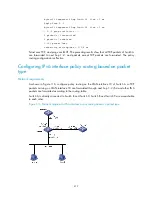
Routing policy configuration
Introduction to routing policy
Routing policy and policy routing
A routing policy is used on a router for route filtering and attributes modification when routes are
received, advertised, or redistributed.
Policy routing, also called PBR, is a routing mechanism based on a user-defined policy.
Routing policy involves both IPv4 routing policy and IPv6 routing policy.
To configure a routing policy, you must define some filters based on the attributes of routing
information, such as destination address, advertising router’s address, and so on. The filters can
be set beforehand and then applied to the routing policy.
Filters
There are several types of filters: ACL, IP prefix list, AS-PATH list, community list, extended
community list, and routing policy
ACL
ACL involves IPv4 ACL and IPv6 ACL. An ACL is configured to match the destinations or next
hops of routing information.
For ACL configuration, see
ACL
in the
ACL and QoS Configuration Guide
.
IP prefix list
IP prefix list involves IPv4 prefix list and IPv6 prefix list.
An IP prefix list is configured to match the destination address of routing information. Moreover,
you can use the
gateway
option to allow only routing information from certain routers to be
received. For
gateway
option information, see
RIP
and
OSPF
in the
Layer 3 – IP Routing
Command Reference.
An IP prefix list, identified by name, can comprise multiple items. Each item, identified by an
index number, can specify a prefix range to match. An item with a smaller index number is
matched first. If one item is matched, the IP prefix list is passed, and the packet will not go to the
next item.