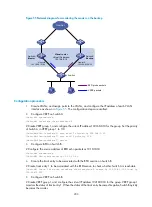
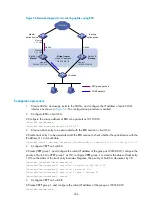
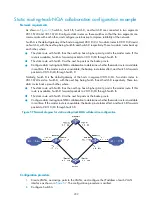
197
Associating track with static routing
A static route is a manually configured route. With a static route configured, packets to the specified
destination are forwarded through the path specified by the administrator.
The disadvantage of using static routes is that they cannot adapt to network topology changes. Faults or
topological changes in the network can make the routes unreachable, causing network breaks.
To prevent this problem, configure another route to back up the static route. When the static route is
reachable, packets are forwarded through the static route; when the static route is unreachable, packets
are forwarded through the backup route, avoiding network breaks and enhancing network reliability.
To check the reachability of a static route in real time, establish association between the track and the
static route.
If you specify the next hop but not the egress interface when configuring a static route, you can establish
collaborations among the static route, the track module, and detection modules. This enables you to
check the reachability of the static route according to the status of the track entry.
•
The Positive state of the track entry shows that the next hop of the static route is reachable, and the
configured static route is valid.
•
The Negative state of the track entry shows that the next hop of the static route is not reachable, and
the configured static route is invalid.
•
The Invalid state of the track entry shows that the reachability of the next hop of the static route is
unknown, and the static route is valid.
Follow these steps to associate track with static routing:
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
Enter system view
system-view
—
ip route-static
dest-address
{
mask
|
mask-length
}
{
next-hop-address
|
vpn-instance
d-vpn-instance-name next-hop-address
}
track
track-entry-number
[
preference
preference-value
]
[
tag
tag-value
] [
description
description-text
]
Associate the static route with
a track entry to check the
reachability of the next hop
ip route-static
vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name&<1-6> dest-address { mask
|
mask-length } { next-hop-address
track
track-entry-number
[
public
] |
vpn-instance
d-vpn-instance-name
next-hop-address
track
track-entry-number
} [
preference
preference-value ]
[
tag
tag-value ] [
description
description-text ]
Required
Use either command.
Not configured by
default.
NOTE:
•
You can associate a nonexistent track entry with a static route. The association takes effect only after you
create the track entry with the
track
command.
•
If the track module detects the next hop reachability of the static route in a private network through
NQA, the VPN instance name of the next hop of the static route must be consistent with that configured
for the NQA test group. Otherwise, the reachability detection cannot function properly.
•
If a static route needs route recursion, the associated track entry must monitor the next hop of the
recursive route instead of that of the static route; otherwise, a valid route may be considered invalid.
•
For more information about static route configuration, see the
Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.