148
Virtual MAC : 0000-5e00-0102
Master IP : 202.38.160.131
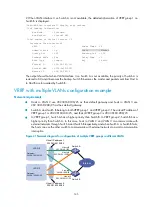
The output shows that in VRRP group 1 Switch A is the master, Switch B is the backup and hosts with the
default gateway of 202.38.160.100/25 accesses the Internet through Switch A; in VRRP group 2 Switch
A is the backup, Switch B is the master and hosts with the default gateway of 202.38.160.200/25
accesses the Internet through Switch B.
VRRP load balancing mode configuration example
Network requirements
•
Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C belong to VRRP group 1 with the virtual IP address of 10.1.1.1/24.
•
Hosts on network segment 10.1.1.0/24 use 10.1.1.1/24 as their default gateway. Use the VRRP
group to ensure that when a gateway—Switch A, Switch B, or Switch C—fails, the hosts on the LAN
can access external networks through another gateway.
•
VRRP group 1 works in load balancing mode to make good use of network resources.
•
Configure a track entry on Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C respectively to monitor their own
VLAN-interface 3. When the interface on Switch A, Switch B, or Switch C fails, the weight of the
corresponding switch decreases so that another switch with a higher weight can take over.
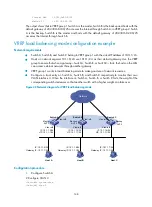
Figure 42
Network diagram for VRRP load balancing mode
Host A
Host B
Host C
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
Vlan-int2
IP: 10.1.1.2/24
VIP: 10.1.1.1/24
Network
Vlan-int2
IP: 10.1.1.3/24
VIP: 10.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int2
IP: 10.1.1.4/24
VIP: 10.1.1.1/24
Master
AVF 1
Backup
AVF 2
Backup
AVF 3
IP: 10.1.1.5/24
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
IP: 10.1.1.6/24
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
IP: 10.1.1.7/24
Gateway IP: 10.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int3
Vlan-int3
Vlan-int3
Configuration procedure
1.
Configure Switch A
# Configure VLAN 2.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] vlan 2