156
Auth Type : None
Virtual IP : 10.1.1.1
Member IP List : 10.1.1.3 (Local, Master)
10.1.1.4 (Backup)
Forwarder Information: 2 Forwarders 1 Active
Config Weight : 255
Running Weight : 255
Forwarder 02
State : Active
Virtual MAC : 000f-e2ff-0012 (Owner)
Owner ID : 0000-5e01-1103
Priority : 255
Active : local
Forwarder 03
State : Listening
Virtual MAC : 000f-e2ff-0013 (Learnt)
Owner ID : 0000-5e01-1105
Priority : 127
Active : 10.1.1.4
Forwarder Weight Track Information:
Track Object : 1 State : Positive Weight Reduced : 250
The output shows that when Switch A fails, Switch B becomes the master because its priority is higher
than that of Switch C.
IPv6-based VRRP configuration examples
This section provides these configuration examples:
•
Single VRRP group configuration example
•
VRRP interface tracking configuration example
•
VRRP with multiple VLANs configuration example
•
VRRP load balancing mode configuration example
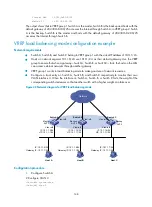
Single VRRP group configuration example
Network requirements
•
Switch A and Switch B belong to VRRP group 1 with the virtual IP addresses of 1::10/64 and
FE80::10.
•
Host A wants to access Host B on the Internet, and learns 1::10/64 as its default gateway through
RA messages sent by the switches.
•
When Switch A operates normally, packets sent from Host A to Host B are forwarded by Switch A;
when Switch A fails, packets sent from Host A to Host B are forwarded by Switch B.