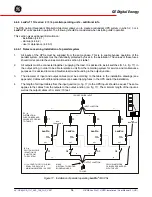
LX: OPM_LPA_11U_5K0_10K_1US_V021
25
GE DE LanPro-11U UPS: Installation / User Manual 2.1 (US)
GE Digital Energy
g
5.3.2 Status and Alarm Menu
The UPS alerts the user with a standard alarm screen that the operating mode has changed and/or that an alarm
situation occurs:
The actual operating mode, the possible modes are mentioned below. The lower
line -if displayed- shows that an alarm occurred. More information can be retrieved
with the 'up' key. If no further information is available, the second line is blank.
Possible operating modes:
21/,1(
The normal operating mode. For more information see section 3.2.
21%<3$66
Overload or failure situation. For more information see section 3.5.
21%$77(5<
For a detailed description of this mode see section 3.3.
2873872))
No power is delivered to the load. This can be the result of a command via the RS232
Port, or because no electric energy is available (utility failure, depleted batteries).
210$18$/%<3$66
Service mode. For more information see section 3.6.
RQ(&2PRGH
ECO-Mode. See section 5.5.5
Depressing the 'up’ key from the standard alarm screen shows, in priority order, which alarms are active,. Scroll
through the screens with the 'up' and 'down' keys. Alarm message texts can succeed each other. The following
messages are possible:
The output capacitor C2 is defective. Contact your dealer.
The load exceeds the rated output power of the UPS, and the output voltage can
no longer be guaranteed. This text alternates with the following screen:
showing the actual load as % of the nominal UPS rating. These messages are
displayed if the load is > 100%.
If the load exceeds 150% the UPS will immediately switch to bypass, assuming
that the conditions for a transfer to bypass are fulfilled. If an overload condition
between 100-150% persists, the UPS can eventually also switch to bypass
operation due to temperature protection. If a transfer to bypass is inhibited (due to
voltage or frequency errors of the utility supply) the UPS may automatically switch
off within a few seconds (load dependent).
Output power is lost at that moment.
To
avoid these problems, be absolutely certain that the power demands of the
protected equipment are within the limits of the UPS.
The temperature of the heatsinks or output transformer is too high. As a result the
output voltage may be transferred to bypass.
The operating temperature can rise to intolerable levels as a result of:
•
extreme environmental temperature
•
lack of proper ventilation
•
an overload situation
•
fan failure
If the UPS operates in 'on line' mode, it will switch to bypass until the temperature is
normal again. If however the UPS operates 'on battery', a shutdown will occur and
output power is lost.
The internal DC voltage is too high, internal failure
The output voltage of the battery charger is too high, internal failure
The battery temperature is too high due to a battery failure or a too high ambient
temperature
21/,1(
$/$5035(6683
/2$'QRW3527(&7('
&$3&'()(&7
83629(5/2$'('
5('8&(/2$'
83629(5/2$'('
/2$'
/2$'QRW3527(&7('
7(03722+,*+
/2$'QRW3527(&7('
92/7$*(722+,*+
%$77(5<&+$5*(5
92/7$*(722+,*+
%$77(5<&+$5*(5
7(03722+,*+