11
Governors America Corp. © 2021 Copyright All Rights Reserved
Enhanced Electronic Governor EEG7000 with GAConfig Tool 8-2021-D6
PIB1009
Once the parameter settings are reviewed and values updated as required, reconnect your fuel supply and start your engine.
1. Reconnect the fuel supply.
2. Crank the engine with DC power applied to the governor system. The engine should be at operating speed with no load.
3.
The actuator/ fuel to the engine will be positioned to the level set by the Actuator Start Fuel (default is maximum fuel). Actuator Ramp
Rate controls the rate at which fuel is increased to start the engine, 10 % by default.
4.
If the engine is unstable after starting, open the GAConfig Tool and adjust the Gain, Stability, and Deadtime in the Engine Tuning
Tuning block, until the engine is relatively stable.
5. Once the engine is stable you can connect additional devices and further tune your engine.
Do not rely exclusively on the governor system electronic actuator to prevent overspeed. A secondary shutoff
device, such as a fuel solenoid must be used.
The STOP - Engine Shutdown button shuts down the controller and actuator, not the engine. STOP shuts
down the voltage to the controller; which disables the PWM output to the actuator; shutting down the engine.
Start YoUr enGine
GETTING STARTED (CONTINUED)
9
To improve basic performance, with no load applied to the engine, complete the following:
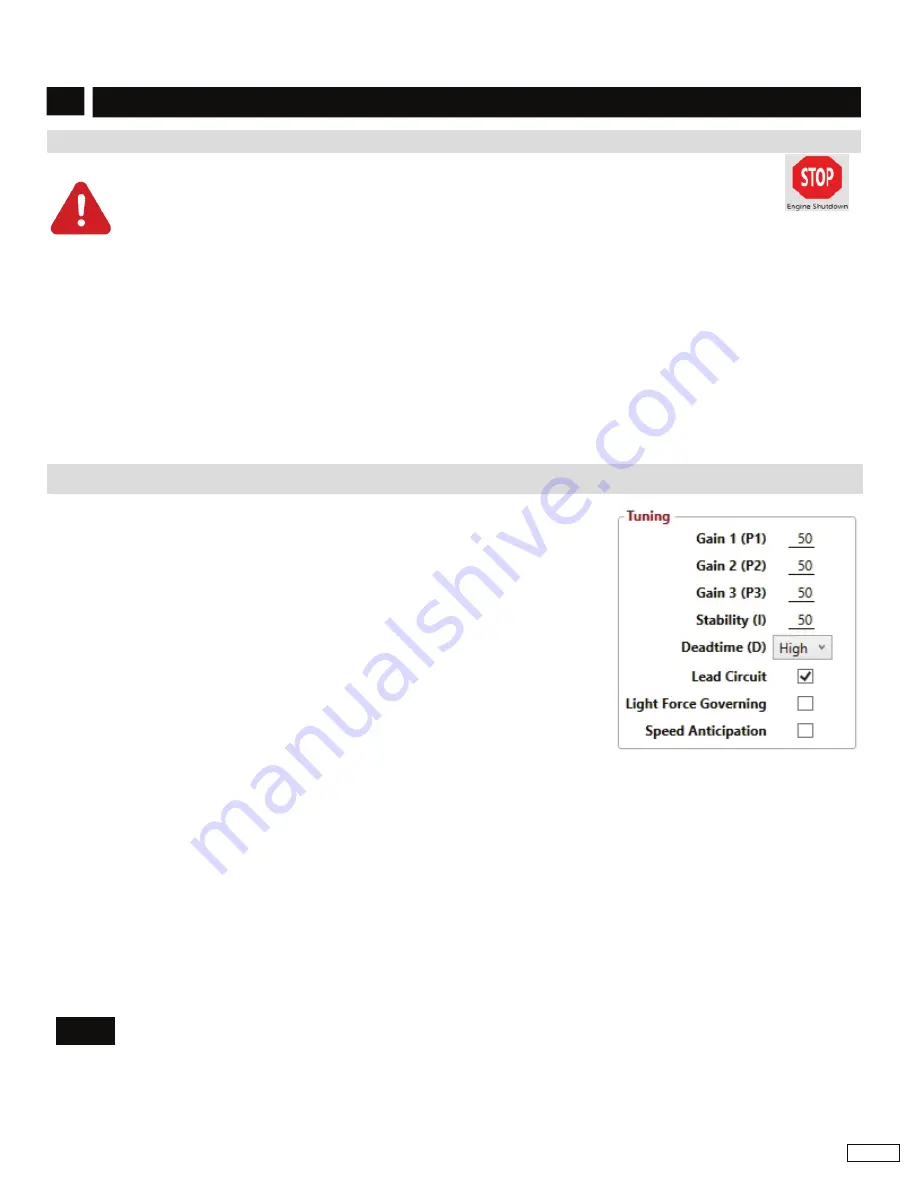
1.
At the GAConfig Tool open the Engine Tuning
Tuning and set the following:
a. Increase the Gain by entering new value until instability develops. Gradually decrease the Gain until stability returns. Decrease
the adjustment one count further to ensure stable performance.
b. Increase Stability value until instability develops. Gradually decrease Stability value until stability returns. Decrease the value by
one to ensure it is stable. If there is no instability leave set at 50.
c. Set the DEADTIME to Low. If instability develops, change to High.
Once the engine is running at operating speed, with no load, use the GAConfig Tool to adjust
the parameter values to increase engine stability. Each speed parameter (Speed 1, 2, 3) has
its own Gain parameter (Gain 1, 2, 3) setting. The speed selection number and active Gain are
.
Stability is achieved by balancing PID: Gain, Stability, and Deadtime.
•
Gain
(Proportional) changes the initial response of the speed controller. Increasing gain
makes the engine more responsive to load changes while decreasing gain makes it less
responsive to load changes. Avoid engine instability due to high gain when adjusting this
parameter. Each fixed speed has a gain value associated with it.
•
Stability
(Integral) changes the steady state response of the engine. Increasing stability
allows the system to come to steady state speed faster, while decreasing the stability
results in a more gradual transition to steady state speed.
•
Deadtime
(Derivative) sets the transient response of the engine to high or low and affects
stability during transient load changes. Increasing deadtime decreases the percent of
overshoot and settling time during a transient load change while decreasing deadtime
increases them.
Setting Deadtime to High can cause random speed instability during steady state since small speed errors
are amplified by this parameter.
Additional adjustments may be required after engine load is applied. Normally, adjustments made at no load achieve
satisfactory performance.
Lead Circuit, Light Force Governing and Speed Anticipation are further described in Section 16,
note
aDjUStinG BaSic StaBilitY WitH fixeD SPeeD






















