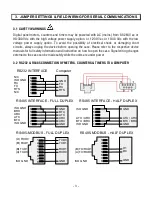
- 16 -
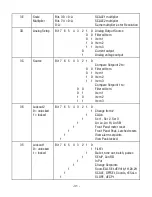
G
Read bytes from RAM Memory
F
Write bytes to RAM Memory (DPM and Scale meter only)
R
Read bytes from Upper RAM Memory
Q
Write bytes to Upper RAM Memory
X
Read words from Non-Volatile Memory
W
Write words to Non-Volatile Memory
CHARACTER 4
Command character
Code #
Code #
Code #
Code #
1 = 1
2 = 2
3 = 3
4 = 4
5 = 5
6 = 6
7 = 7
8 = 8
9 = 9
A = 10
B = 11
C = 12
D = 13
E = 14
F = 15
G = 16
H = 17
I = 18
J = 19
K = 20
L = 21
M = 22
N = 23
O = 24
P = 25
Q = 26
R = 27
S = 28
T = 29
U = 30
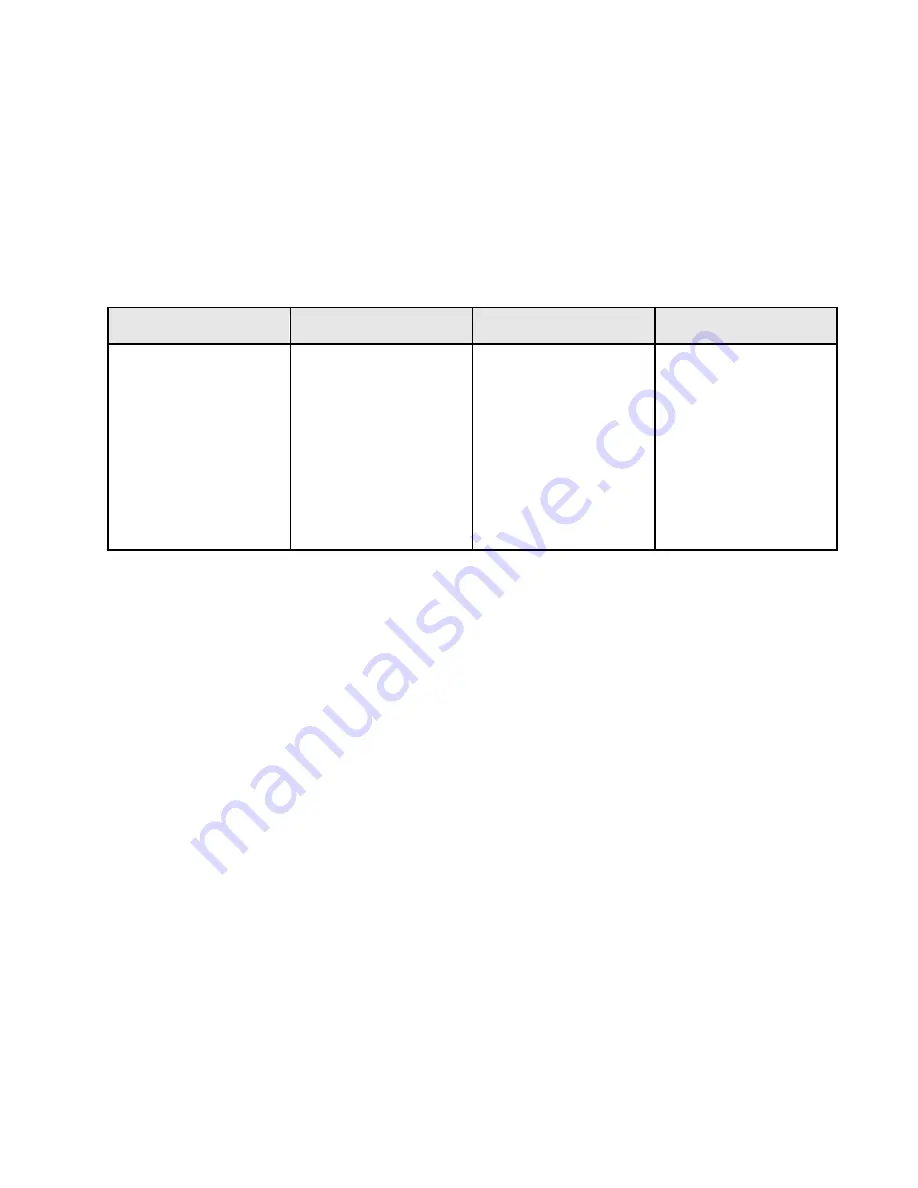
CHARACTERS 5, 6
See tables for the RAM MEMORY ADDRESSES and NONVOLATILE MEMORY ADDRESSES with
their respective data definitions.
GENERAL, READING AND WRITING RAM MEMORY DATA
RAM memory data is read and written as a continuous string of bytes consisting of 2 hex
characters (0-9,A-F) per byte. Included in the command are the total number of bytes to be
transferred and the most significant address in RAM of the continuous string of bytes. The
format is:
Read lower RAM data *1Gnaa
Write lower RAM data *1Fnaa<data>
Read upper RAM data *1Rnaa
Write upper RAM data *1Qnaa<data>
where: n
is the number of bytes to be read or written.
aa
is the most significant address in RAM of the bytes to be read or written.
<data>
is n bytes of 2 hex characters per byte in order from the most to the least
significant byte.
The number of bytes n consists of a single code character representing values from 1 to 30 as
shown above under CHARACTER 4. The most significant address aa consists of 2 hex charac-
ters as shown below under RAM MEMORY ADDRESSES AND DATA DEFINITIONS.