The safety function STO is used when, in the application, the energy supply to the motor should be
safely switched off but there are no further requirements for a targeted standstill of the drive (such
as stop category 1 from EN 60204-1
è
Function and application STO
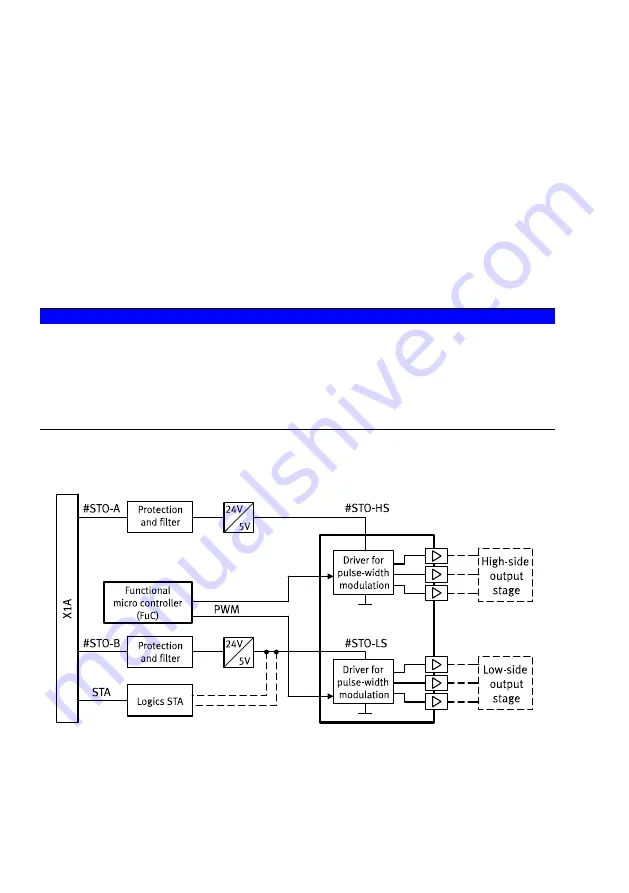
The safety function STO switches off the driver supply for the power semiconductor, thus preventing
the power end stage from supplying the energy required by the motor. The power supply to the drive
is safely disconnected when the safety function STO is active. The drive cannot generate torque and so
cannot make any hazardous movements. With suspended loads or other external forces, additional
measures must be taken to ensure that the load does not drop (e.g. mechanical clamping units). In
the STO status, the standstill position is not monitored.
The machines must be stopped and locked in a safe manner. This especially applies to vertical axles
without automatic locking mechanics, clamping units or counterbalancing.
NOTICE!
If there are multiple errors in the servo drive, there is a danger that the drive will move. Failure of the
servo drive output stage during the STO status (simultaneous short circuit of 2 power semiconductors
in different phases) may result in a limited detent movement of the rotor. The rotation angle/travel
corresponds to a pole pitch. Examples:
•
Rotating motor, synchronous machine, 8-pin
è
Movement
<
45° at the motor shaft
•
Linear motor, pole pitch 20 mm
è
Movement
<
20 mm at the moving part
Functional principle STO
Fig. 2 Functional principle STO
Product overview
8
Festo — CMMT-AS-...-S1 — 2018-02























