RELEASED: 10/2/2006
Page 23
COMMUNICATI0NS
HSD SERIES OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE
This is an unpublished work protected by the United States copyright laws and is proprietary to EMCEE Communications.
Disclosure, copying, reproduction, merger, translation, modification, enhancement or use by anyone other than authorized
employees or licensees of EMCEE Communications without the prior written consent of EMCEE Communications is strictly
prohibited.
Copyright © 2006 EMCEE Communications. All rights reserved.
This copyright notice should not be construed as evidence of publication.
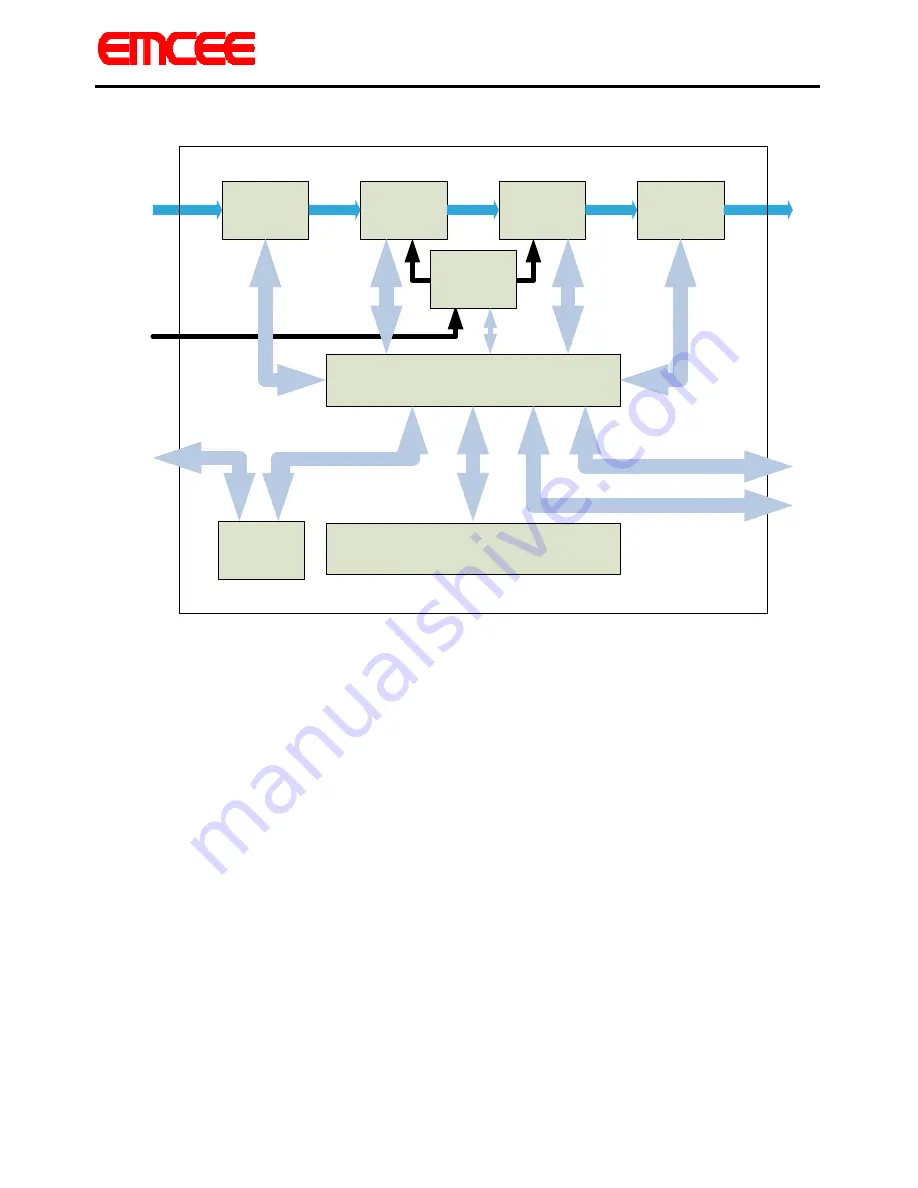
3.1.1 Up-Converter Block Diagram:
1
st
IF
MODULE
A1
1
st
CONVERTER
MODULE
A2
OUTPUT
CONVERTER
MODULE
A3
DRIVER
AMP
MODULE
A4
CONTROL BOARD
PC2
DISPLAY BOARD
PC1
IF
RF
IF
IF IN
STAT
US/
C
ONTROL
S
TATUS
/CO
NTROL
STAT
US/
C
ONTROL
S
TATUS
/CO
NTROL
ST
ATUS/
CONT
ROL
RF OUT
UP-CONVERTER DRAWER, D1
EXT. REF.
POWER AMP STATUS/CONTROL
P/S STATUS/CONTROL
10 MHz
REFERENCE
MODULE
A5
ST
ATU
S
/C
ON
TR
OL
REMOTE
CONTROL
BOARD
PC3
STATUS/CONTROL
REMOTE
STATUS/CONTROL
3.2 1
st
IF Module:
P/N 50521000
Schematic Diagram 50521002A, D1A1
The first IF module receives the composite analog or digital modulator output at
input J1, over a range of -5 to -25dBm. The first IF module performs the following
five important functions. First, it provides for AGC control of the incoming IF signal
and additional overdrive protection. Second, it provides the Operate/Standby
functionality. Third it provides output level control. Fourth, it provides linearity
correction. Lastly, it provides output AGC control.
The input AGC loop holds the input signal level constant regardless of the input
level, as long as the input range is between -5 and -25 dBm, allowing for a wide
variety of modulators to be used without requiring resetting other levels in the
transmitter. The AGC loop utilizes the pin diode attenuator network formed around
















































