3.2. Inspection
3.2.1. Cylinder block
1) Clean the cylinder block thoroughly and make a visual inspection for cracks or damage.
2) Replace if cracked or severely damaged, and correct if slightly damaged.
3) Check oil and water flow lines for restriction or corrosion.
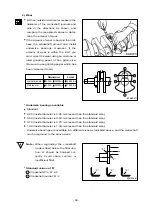
4) Make a hydraulic test to check for any cracks or air leaks.(Hydraulic test) :
Stop up each outlet port of water/oil passages in the cylinder block, apply air pressure of
about 4kg/cm
2
against the inlet ports, then immerse the cylinder block in water for about 1
minute to check any leaks. (Water temperature: 70
˚
C)
3.2.2. Cylinder head
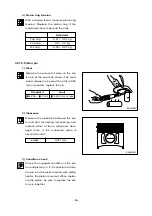
1) Inspection
•
Carefully remove carbon from the lower lace of the cylinder head using nonmetallic mater-
ial to prevent scratching of the valve seat faces.
•
Check the entire cylinder head for very fine cracks or damage invisible to ordinary sight
using a hydraulic tester or a magnetic flaw detector.
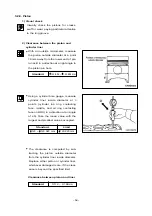
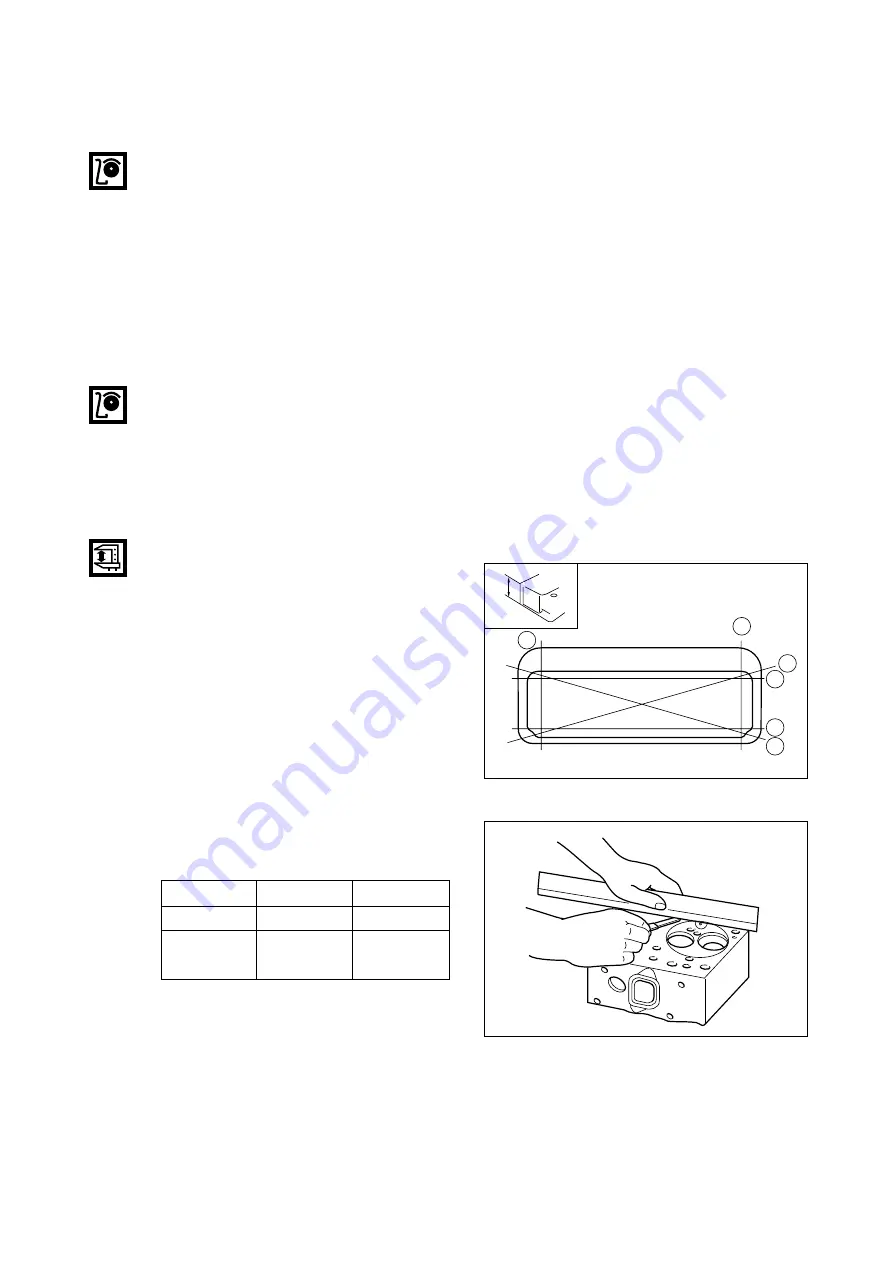
2) Distortion at the lower face
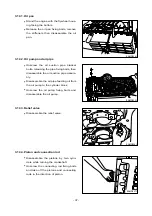
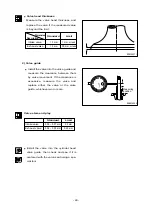
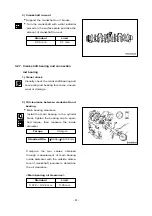
•
Measure the amount of distortion using
a straight edge and a feeler gauge at six
positions (A ~ F) as shown in the right
figure.
•
If the measured value exceeds the stan-
dard value, retrace the head with grind-
ing paper of fine grain size to correct
such defect.
•
If the measured value exceeds the max-
imum allowable limit, replace the cylin-
der head.
Lower face warpage and height
- 41 -
(t)
A
B
C
D
E
EA3M2031
F
EA6M2002
Standard
Limit
Warpage
0.2 mm or less
0.3 mm
Thickness : t
(reference)
114.95 ~ 115.0 mm
113.9 mm