33
SIP Operation Manual V2.6
NAT/DDNS
NAT Traversal
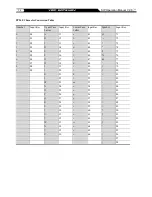
If a Gateway is set up under an IP sharing setting, you can select either the NAT or STUN protocol.
NAT Public IP: The IP address used by the gateway should be a virtual address. Further more, users
must set the Virtual Server Mapping in the NAT Server (A virtual server is defined as a Service Port,
and all requests to this port will be redirected to this specified the server IP address).
The default port is listed below:
Listen Port (UDP): 5060
RTP Starting Port (UDP): 9000~9015 (Listen Port used for telephone communication).
Http Port (TCP): 80
NAT IP/Domain: Enter the NAT Server IP address (Real External IP address of NAT Server) then
fill in the URL (Uniform Resource Locator). If using DDNS, please refer to the next setting item
Enable STUN Client: Using STUN protocol prevents problems with setting the IP sharing function,
but some NAT do not support this protocol.
STUN Server IP/Domain and Port: Enter the STUN server IP address and Listen Port number. You
can set 2 STUN server spread by semicolon.
Enable UPnP Control Point: To enable the VoIP gateway’s IP traffic to pass through a NAT server.
This function only works when the NAT server supports UPnP and has it enabled.
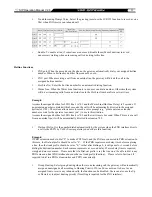
DDNS
These settings are only necessary when the gateway is set up under a NAT that uses a dynamic IP address
and do not support DDNS.
Choose a DDNS Server: The current system allows users to choose either DynDNS
、
TZO
、
3322.org
、
PeanutHull or a private server. Please apply for a user account before choosing a service provider.
Server address: Sets up the IP address or URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of the DDNS Server.
Hostname: The URL of the system (or NAT) – apply from a domain name registration providers.
Login ID and Password: The ID and password are used to log into the DDNS server.
Behind NAT: Select only when the system is set up under NAT.
NOTE: If the Gateway is set up under NAT, then enter the hostname into the NAT IP/Domain.