DIR-620S
Wireless N300 Router with 3G/LTE Support and
USB Port
User Manual
Configuring via Web-based Interface
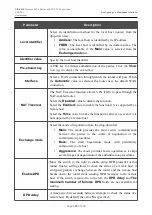
DMZ
A DMZ is a host or network segment located “between” internal (local) and external (global)
networks. In the router, the DMZ implements the capability to transfer a request coming to a port of
the router from the external network to a specified host of the internal network.
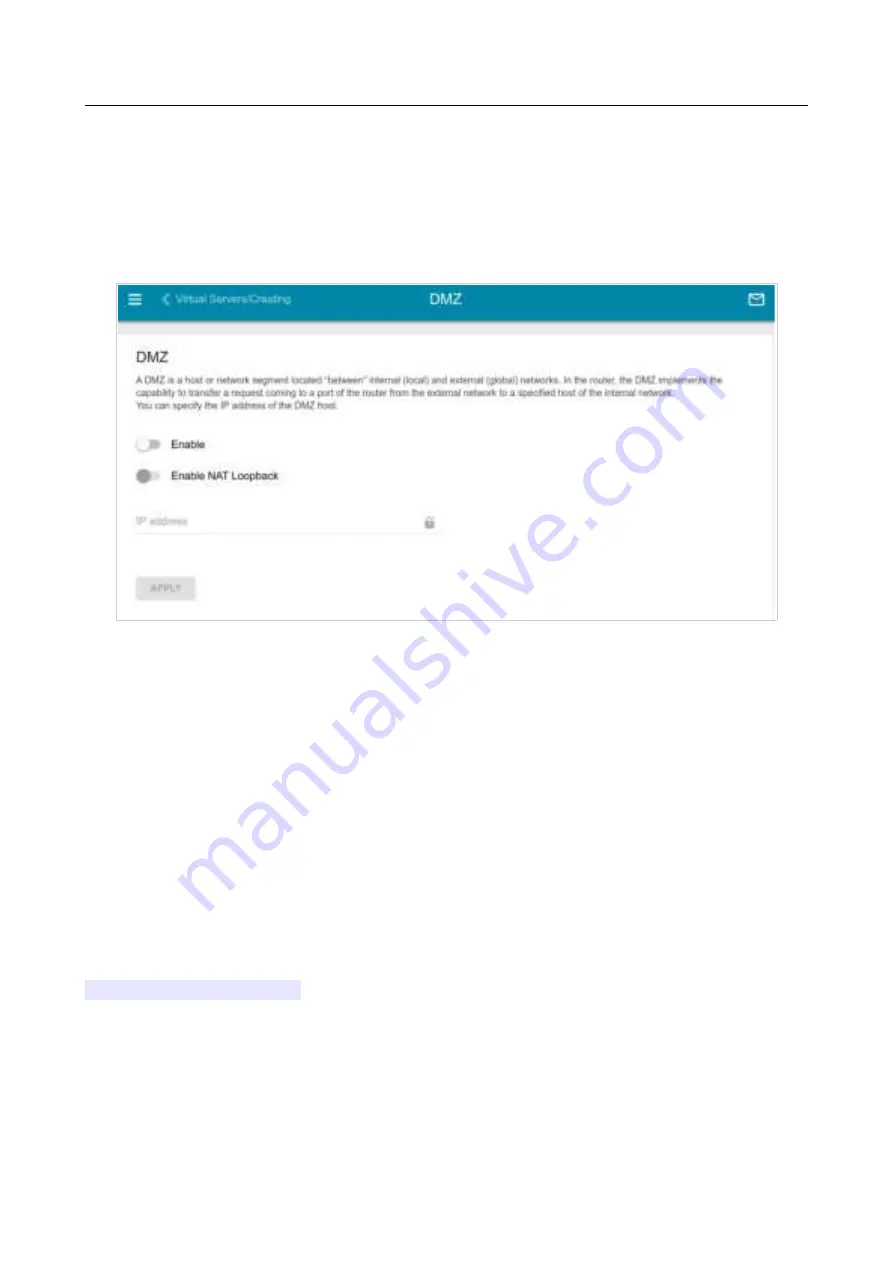
On the
Firewall / DMZ
page, you can specify the IP address of the DMZ host.
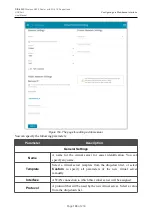
Figure 160. The
Firewall / DMZ
page.
To enable the DMZ, move the
Enable
switch to the right.
Enter the IP address of a host from your network in the
IP address
field. To choose a device
connected to the router's LAN at the moment, select the relevant value from the drop-down list (the
field will be filled in automatically).
Move the
Enable NAT Loopback
switch to the right in order to let the users of the router's LAN
access the DMZ host using the external IP address of the router or its DDNS name (if a DDNS
service is configured). Users from the external network access the router using the same address (or
DDNS name).
Click the
APPLY
button.
Note that when the DMZ is enabled, all traffic coming to a port of the WAN interface of the router
is directed to the same port of the specified IP address. Also note that virtual servers have higher
priority than the DMZ host. In other words, if there has been created a virtual server that directs
traffic from external port 80 to a port of the device from the router's local network, then entering
http://router_WAN_IP
in the address bar, users of the external network are directed to the
specified port and IP address configured for the virtual server, but not to port 80 of the device with
the IP address specified on the
Firewall / DMZ
page.
To disable the DMZ, move the
Enable
switch to the left and click the
APPLY
button.
Page
201
of 236