D-Link DES-3350SR Standalone Layer 3 Switch
121
a value of 0 is entered, the Switch will not
process the value in the seconds field of
the BOOTP or DHCP packet. If a non-zero
value is entered, the Switch will use that
value, along with the hop count to
determine whether to forward a given
BOOTP or DHCP packet.
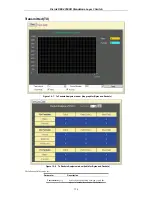
DHCP/BOOTP Relay Interface Settings
The
DHCP/ BOOTP Relay Interface Settings
allow the user to set up a server, by IP address, for relaying DHCP/ BOOTP
information to the Switch. The user may enter a previously configured IP interface on the Switch that will be connected directly to
the DHCP/BOOTP server using the following window. Properly configured settings will be displayed in the
BOOTP Relay Table
at the bottom of the following window, once the user clicks the
Add
button under the
Apply
heading. The user may add up to four
server IPs per IP interface on the Switch.
Figure 9 - 38. DHCP/BOOTP Relay Settings and DHCP/BOOTP Relay Table
The following parameters may be configured or viewed.
Parameters Description
Interface
The IP interface on the Switch that will be
connected directly to the Server.
Server IP
Enter the IP address of the DHCP/BOOTP
server. Up to four server IPs can be
configured per IP Interface
DNS Relay
Computer users usually prefer to use text names for computers for which they may want to open a connection. Computers
themselves, require 32 bit IP addresses. Somewhere, a database of network devices’ text names and their corresponding IP
addresses must be maintained.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to map names to IP addresses throughout the Internet and has been adapted for use
within intranets.
For two DNS servers to communicate across different subnets, the
DNS Relay
of the Switch must be used. The DNS servers are
identified by IP addresses.
Mapping Domain Names to Addresses
Name-to-address translation is performed by a program called a Name Server. The client program is called a Name Resolver. A
Name Resolver may need to contact several Name Servers to translate a name to an address.
The Domain Name System (DNS) servers are organized in a somewhat hierarchical fashion. A single server often holds names for
a single network, which is connected to a root DNS server - usually maintained by an ISP.
Domain Name Resolution
The domain name system can be used by contacting the name servers one at a time, or by asking the domain name system to do the
complete name translation. The client makes a query containing the name, the type of answer required, and a code specifying
whether the domain name system should do the entire name translation, or simply return the address of the next DNS server if the
server receiving the query cannot resolve the name.
When a DNS server receives a query, it checks to see if the name is in its sub domain. If it is, the server translates the name and
appends the answer to the query, and sends it back to the client. If the DNS server cannot translate the name, it determines what
type of name resolution the client requested. A complete translation is called recursive resolution and requires the server to contact
Содержание DES-3350SR
Страница 1: ...D Link DES 3350SR Standalone Layer 3 Switch User s Guide...
Страница 80: ...D Link DES 3350SR Standalone Layer 3 Switch 70 Figure 7 57 The Client...
Страница 138: ...D Link DES 3350SR Standalone Layer 3 Switch 128 Click Apply to implement changes made...
Страница 160: ...D Link DES 3350SR Standalone Layer 3 Switch 150 Figure 10 33 PIM Neighbor Table...
Страница 188: ......