File name : CBM_SR-281N_IB_English_black_v09330.doc
Date: 2009/3/30 Trimmed Size : 140 x 75 mm SCALE 1 : 1
-E26-
In the binary base, the block 1 is displayed immediately after
calculation. Other blocks ( block 2 ~ block 4 ) are displayed by pressing
[
].
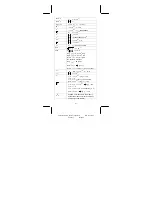
For example, input 47577557
16
Press [ 2nd ] [ HEX ] 47577557
[ 2nd ] [ BIN ]
0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
b
DEG BIN
– –
Indicates Block 1 presently displayed
[
]
0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1
b
DEG BIN
–
–
Indicates Block 2 presently displayed
[
]
0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
b
DEG BIN
– –
Indicates Block 3 presently displayed
[
]
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1
b
DEG BIN
– – –
Indicates Block 4 presently displayed
47577557
16
= Block 4 + Block 3 + Block 2 + Block 1
= 01000111010101110111010101010111
2
Basic arithmetic operations for bases
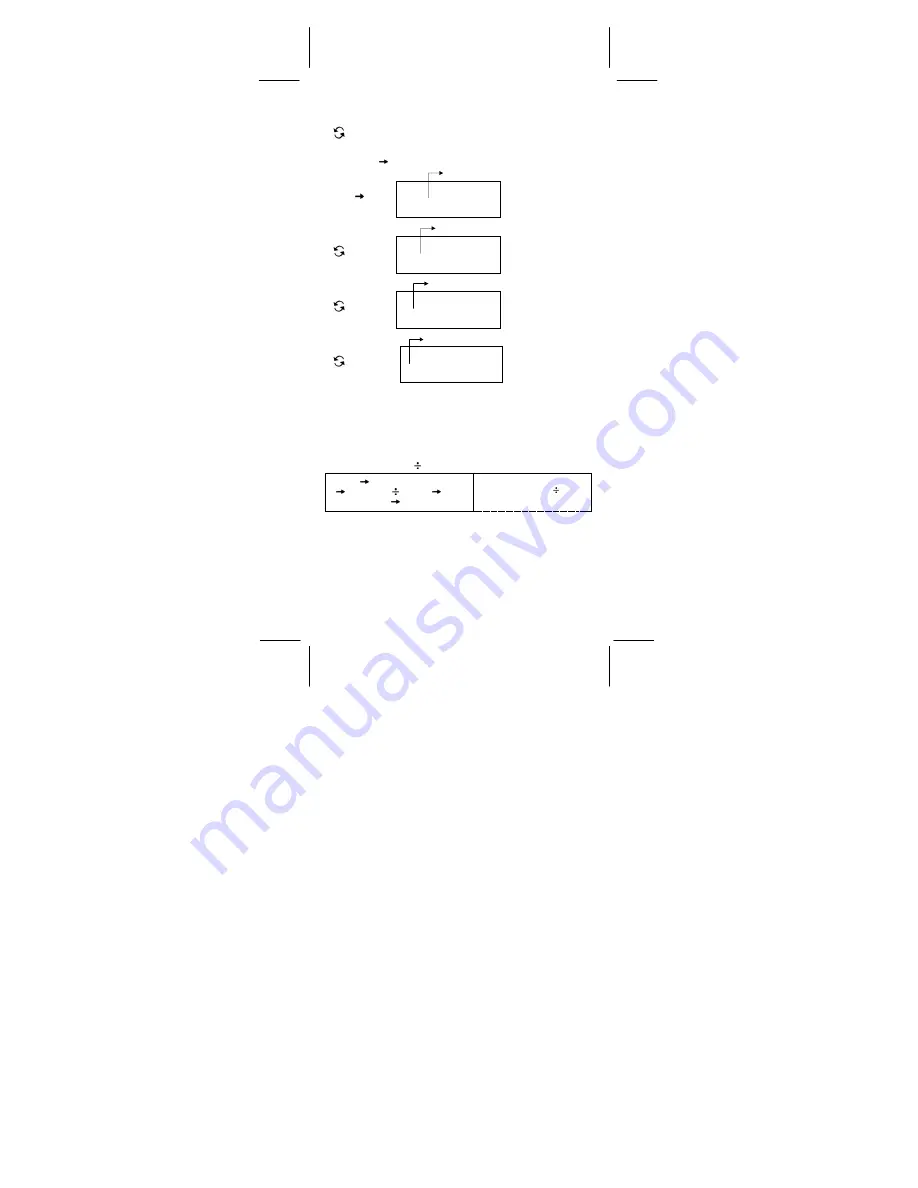
¾
1IEIF
16
+ 1234
10
1001
2
= 1170
8
DEG
OCT
h 1 IE IF + 1 2 3 4
b 1
[ 2nd ] [ HEX ] 1E F [ + ] [ 2nd ]
[ DEC ] 1234 [ ] [ 2nd ] [ BIN ]
1001 [=] [ 2nd ] [ OCT ]
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 7 0
o
Negative expressions
In binary, octal, and hexadecimal bases, the calculator represents
negative numbers using complement notation.
The complement is the result of subtracting that number from
100000000000000000000000000000000 in that number's base by
pressing [ NEG ] key in non-decimal bases.