The switch is synchronized with superior root information received on the root port if all other ports are
synchronized. An individual port on the switch is synchronized if either of the following applies:
•
That port is in the blocking state.
•
It is an edge port (a port configured to be at the edge of the network).
If a designated port is in the forwarding state and is not configured as an edge port, it transitions to the blocking
state when the Rapid PVST+ forces it to synchronize with new root information. In general, when the Rapid
PVST+ forces a port to synchronize with root information and the port does not satisfy any of the above
conditions, its port state is set to blocking.
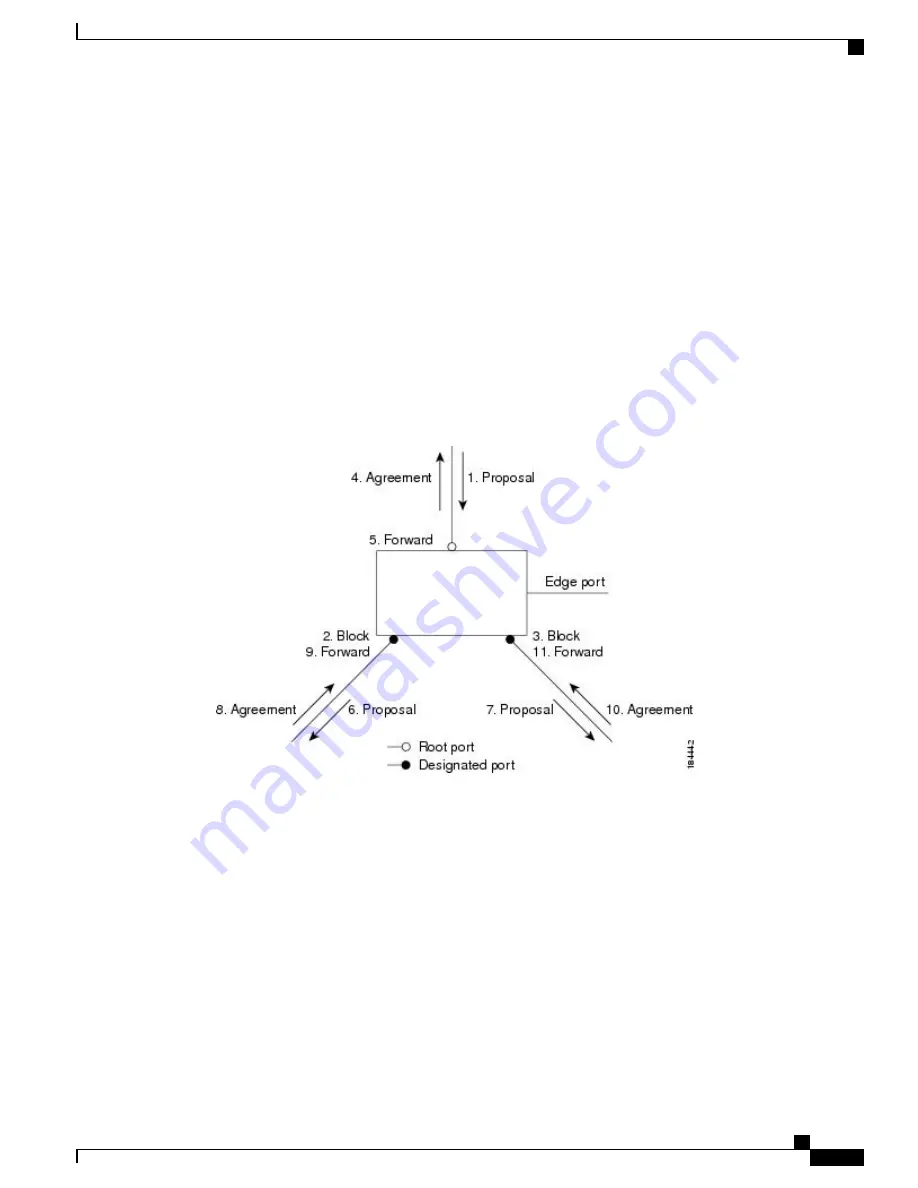
After ensuring that all of the ports are synchronized, the switch sends an agreement message to the designated
switch that corresponds to its root port. When the switches connected by a point-to-point link are in agreement
about their port roles, Rapid PVST+ immediately transitions the port states to the forwarding state. The
sequence of events is shown in the following figure.
Figure 11: Sequence of Events During Rapid Convergence
Processing Superior BPDU Information
A superior BPDU is a BPDU with root information (such as a lower switch ID or lower path cost) that is
superior to what is currently stored for the port.
If a port receives a superior BPDU, Rapid PVST+ triggers a reconfiguration. If the port is proposed and is
selected as the new root port, Rapid PVST+ forces all the other ports to synchronize.
If the received BPDU is a Rapid PVST+ BPDU with the proposal flag set, the switch sends an agreement
message after all of the other ports are synchronized. The new root port transitions to the forwarding state as
soon as the previous port reaches the blocking state.
If the superior information received on the port causes the port to become a backup port or an alternate port,
Rapid PVST+ sets the port to the blocking state and sends an agreement message. The designated port continues
sending BPDUs with the proposal flag set until the forward-delay timer expires. At that time, the port transitions
to the forwarding state.
Cisco Nexus 6000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 7.x
55
Configuring Rapid PVST+
Understanding Rapid PVST+
















































