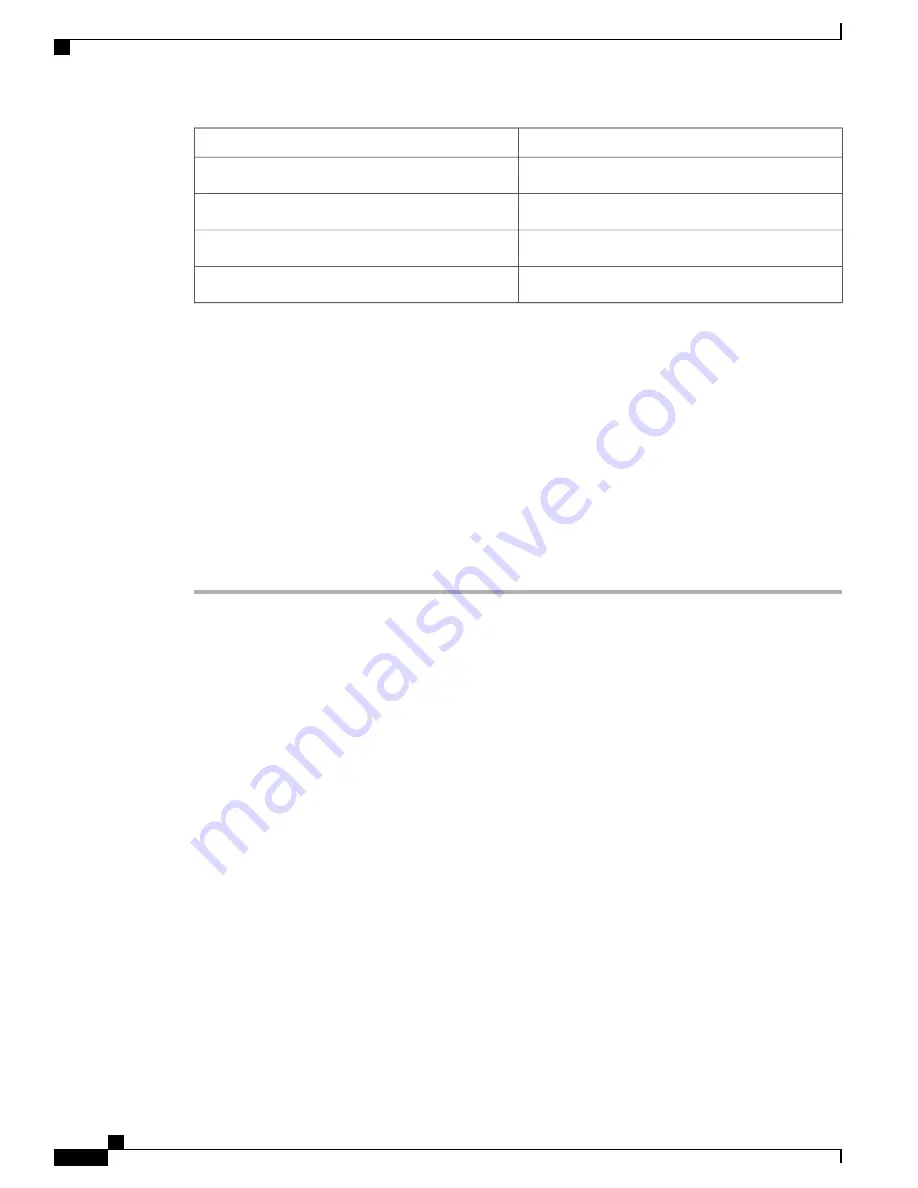
Default
Parameters
Enabled
LLDP
Disabled
vPC
Enabled
svs vethernet auto-setup
Disabled
FCoE
Configuring VM-FEX
Overview of the VM-FEX Configuration Steps
The following steps outline the necessary sequence of procedures for configuring VM-FEX between the
switch and the server hosting the VMs. Procedures to be performed on the switch are described in this document.
For procedures to be performed on the server or the VMware vCenter, refer to the server and vCenter
documentation.
Procedure
Step 1
Server: Create vNICs on VIC adapter.
a) Create two static vNICs to be used as uplinks from the host.
b) Create up to 112 VM-FEX interfaces.
c) Reboot the server.
Step 2
Switch: Enable VM-FEX and other required services.
See
Enabling Features Required for VM-FEX, on page 189
.
Step 3
Switch: Configure two static vEthernet interfaces and bind them to the physical port and channel.
See
Configuring the Fixed Static Interfaces, on page 190
.
Step 4
Switch: Define port profiles to be associated with the VMs.
See
Configuring a Port Profile for the Dynamic Interfaces, on page 193
.
Step 5
Switch: Verify that the two static vEthernet interfaces are active and associated with the vEthernet interfaces
of the switch.
See
Verifying the Status of the Virtual Interfaces, on page 196
.
Step 6
Switch and vCenter: Install XML certificate from switch to vCenter.
a) Switch: Enable HTTP using the
feature http
command in global configuration mode.
b) From a web browser, access the IP address of the switch and download the displayed XML certificate.
c) Switch: Disable HTTP using the
no feature http
command in global configuration mode.
d) vCenter: Install the XML certificate plugin.
Step 7
Switch: Enable vPC and register the vPC system to the vCenter as a distributed virtual switch (DVS).
See
Configuring an SVS Connection to the vCenter Server, on page 194
.
Cisco Nexus 6000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 7.x
188
Configuring VM-FEX
Configuring VM-FEX
















































