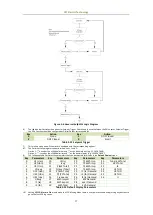
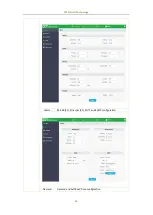
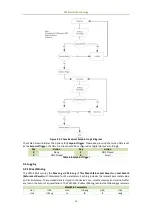
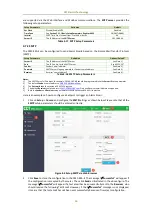
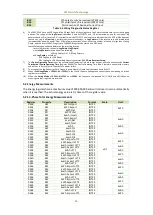
CET Electric Technology
42
THDf:
THD
f
=
√∑
I
n
2
∞
n=2
I
1
×100%
THDr:
THDr
=
√∑
I
n
2
∞
n=2
√∑
I
n
2
∞
n=1
×100%
where I
1
represents the RMS value of the fundamental component, and I
n
represents the RMS
value for the n
th
harmonic.
4.3.3.2 TDD
Total Demand Distortion (TDD) is defined as the ratio of the RMS of the Harmonic Current to the RMS
of the Rated or Maximum Fundamental Current Demand.
TDD of Current is calculated by the formula below:
𝑇𝐷𝐷 =
√∑
𝐼
𝑛
2
∞
𝑛=1
𝐼
𝐿
× 100%
where
I
L
= Maximum Fundamental Current Demand
n
= Harmonic Order (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.)
I
n
= RMS Load Current at the n
th
Harmonic
4.3.3.3 K-Factor
K-Factor is defined as the weighted sum of the Harmonic Load Current according to their effects on
transformer heating, as derived from ANSI/IEEE C57.110. A K-Factor of 1.0 indicates a linear load (no
harmonics). The higher the K-Factor, the greater the harmonic heating effect.
K − Factor =
∑
(I
n
∙ n)
2
n=n
max
n=1
∑
I
n
2
n=n
max
n=1
where
I
n
= n
th
Harmonic Current in RMS
n
max
=Highest Harmonic order
4.3.3.4 Crest Factor
Crest Factor is defined as the Peak to Average Ratio (PAR), and its calculation is illustrated below:
C=
|
X
|
peak
X
rms
where
|X|
peak
= Peak amplitude of the waveform
X
rms
= RMS value