19
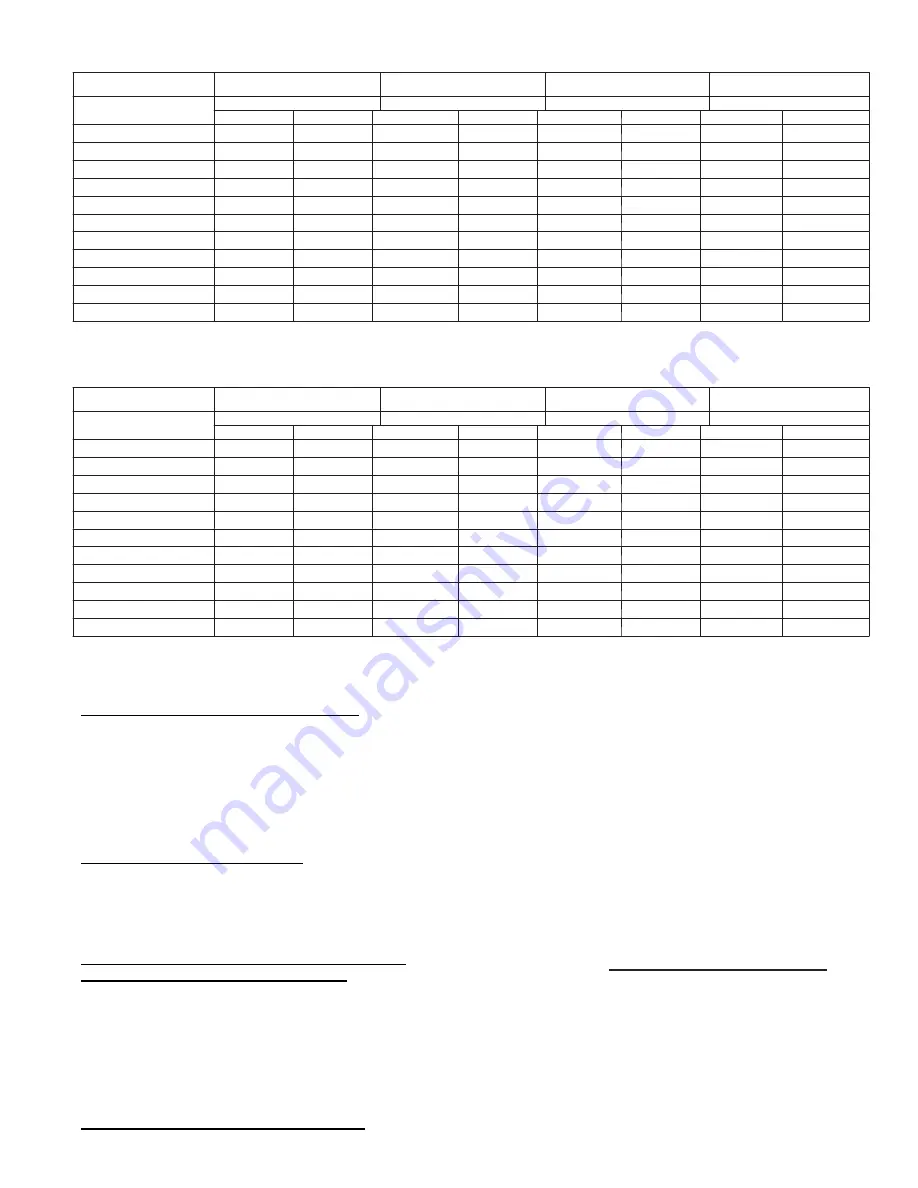
Table 5—Natural Gas
NOMINAL INPUT
200,000
175,000
150,000
125,000
Altitude
Vent Lengths
Vent Lengths
Vent Lengths
Vent Lengths
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
0
200,000
200,000
175,000
175,000
150,000
150,000
125,000
125,000
1,000
197,000
196,500
172,400
172,200
147,800
147,400
123,500
123,000
2,000
194,000
193,000
169,800
169,400
145,600
144,800
122,000
121,000
3,000
191,000
189,500
167,200
166,600
143,400
142,200
120,500
119,000
4,000
188,000
186,000
164,600
163,800
141,200
139,600
119,000
117,000
5,000
185,000
182,500
162,000
161,000
139,000
137,000
117,500
115,000
6,000
182,000
179,000
159,400
158,200
136,800
134,400
116,000
113,000
7,000
179,000
175,500
156,800
155,400
134,600
131,800
114,500
111,000
8,000
176,000
172,000
154,200
152,600
132,400
129,200
113,000
109,000
9,000
173,000
168,500
151,600
149,800
130,200
126,600
111,500
107,000
10,000
170,000
165,000
149,000
147,000
128,000
124,000
110,000
105,000
Table 6—LP Gas
NOMINAL INPUT
200,000
175,000
150,000
125,000
Altitude
Vent Lengths
Vent Lengths
Vent Lengths
Vent Lengths
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
0
200,000
200,000
175,000
175,000
150,000
150,000
125,000
125,000
1,000
195,900
195,750
171,900
171,200
146,900
146,700
123,050
122,250
2,000
191,800
191,500
168,800
167,400
143,800
143,400
121,100
119,500
3,000
187,700
187,250
165,700
163,600
140,700
140,100
119,150
116,750
4,000
183,600
183,000
162,600
159,800
137,600
136,800
117,200
114,000
5,000
179,500
178,750
159,500
156,000
134,500
133,500
115,250
111,250
6,000
175,400
174,500
156,400
152,200
131,400
130,200
113,300
108,500
7,000
171,300
170,250
153,300
148,400
128,300
126,900
111,350
105,750
8,000
167,200
166,000
150,200
144,600
125,200
123,600
109,400
103,000
9,000
163,100
161,750
147,100
140,800
122,100
120,300
107,450
100,250
10,000
159,000
157,500
144,000
137,000
119,000
117,000
105,500
97,500
NOTE: The boiler automatically derates input as altitude increases. No alterations to boiler are required for altitudes above sea level.
These low pressure gas---fired hot water boilers are design certified by CSA International, for use with natural and propane gases. The boilers are constructed
and hydrostatically tested for a maximum working pressure of 50 psig (pounds per square inch gauge) in accordance with A.S.M.E. (American Society of
Mechanical Engineers) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section IV Standards for heating boilers.
TEST HIGH LIMIT CONTROL AND ADJUST
While burner is operating, Adjust setting on high limit control
below actual boiler water temperature. Burner should go off while
circulator continues to operate. Raise limit setting above boiler
water temperature and burner should reignite after pre purge and
igniter warm--up period. Set the high limit control to the design
temperature requirements of the system. Maximum high limit
setting is 200
_
F. Minimum high limit setting is 100
_
F. Return
high limit differential to original setting of 20
_
F.
TEST OTHER SAFETY CONTROLS
If the boiler is equipped with a low water cut off, a manual reset
high limit, or additional safety controls, test for operation as
outlined by the control manufacturer. Burner should be operating
and should go off when controls are tested. When safety controls
are restored, burner should reignite.
SET THERMOSTAT HEAT ANTICIPATOR (IF USED)
AND VERIFY THERMOSTAT OPERATION
For a single thermostat connected to the yellow thermostat lead
wires in the furnished field wiring junction box, the heat
anticipator should be set at 0.7 amps. For other wiring
configurations, refer to the instructions provided by the
thermostat manufacturer regarding adjustment of heat anticipator.
Cycle boiler with thermostat. Raise the thermostat to the highest
setting and verify boiler goes through normal start up cycle.
Lower thermostat to lowest setting and verify boiler goes off.
MEASURE THE NATURAL GAS INPUT RATE
Correct input rate is essential for proper and efficient operation of
the burner and boiler.
1. Determine elevation at installation site.
2. See Table 5 and 6 to determine the correct approximate
input rate for the local elevation.
3. Obtain the yearly average heating value of the local gas
supply from the gas utility. At sea level elevation, it should
be approximately 1000 Btu’s per standard cubic foot.
4. Operate boiler for 5 minutes.
5. Turn off all other gas appliances, extinguishing standing
pilots where applicable.
6. At gas meter, measure time in seconds required to use one
cubic foot of gas.
7. Calculate “input rate” according to the following formula:
Btuh input rate = 3600 x heating value from step 3
time from step 6
8. The measured input rate should be /--2 percent of
the input rating from step 2. If not, see the
ADJUSTMENTS section.
















































