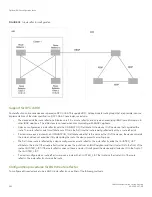
device(config-bgp)# neighbor abc remote-as 2
device(config-bgp)#
neighbor abc enforce-first-as disable
device(config-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.1.2 peer-group abc
device(config-bgp)#
neighbor 192.168.1.2 enforce-first-as enable
Disabling or re-enabling comparison of the AS-Path length
AS-Path comparison is Step 5 in the algorithm that BGP4 uses to select the next path for a route. Comparison of the AS-Path length is
enabled by default. To disable it, enter the following command at the BGP4 configuration level of the CLI.
device(config-bgp)# as-path-ignore
Syntax:
[no] as-path-ignore
This command disables comparison of the AS-Path lengths of otherwise equal paths. When you disable AS-Path length comparison, the
BGP4 algorithm shown in
How BGP4 selects a path for a route (BGP best path selection algorithm)
on page 353 skips from Step 4 to
Step 6.
Enabling or disabling comparison of device IDs
Device ID comparison is Step 10 in the algorithm BGP4 uses to select the next path for a route.
NOTE
Comparison of device IDs is applicable only when BGP4 load sharing is disabled.
When device ID comparison is enabled, the path comparison algorithm compares the device IDs of the neighbors that sent the otherwise
equal paths:
•
If BGP4 load sharing is disabled (maximum-paths 1), the instructions in this section selects the path that came from the
neighbor with the lower device ID.
•
If BGP4 load sharing is enabled, the device load shares among the remaining paths. In this case, the device ID is not used to
select a path.
NOTE
Device ID comparison is disabled by default.
To enable device ID comparison, enter the
compare-routerid
command at the BGP4 configuration level of the CLI.
device(config-bgp-router)# compare-routerid
Syntax:
[no] compare-routerid
Configuring the device to always compare Multi-Exit Discriminators
A Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) is a value that the BGP4 algorithm uses when it compares multiple paths received from different BGP4
neighbors in the same AS for the same route. In BGP4, a MED for a route is equivalent to its metric.
BGP4 compares the MEDs of two otherwise equivalent paths if and only if the routes were learned from the same neighboring AS. This
behavior is called deterministic MED. Deterministic MED is always enabled and cannot be disabled.
You can enable the device to always compare the MEDs, regardless of the AS information in the paths. For example, if the device
receives UPDATES for the same route from neighbors in three autonomous systems, the device can compare the MEDs of all the paths
together instead of comparing the MEDs for the paths in each autonomous system individually.
Optional BGP4 configuration tasks
FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing
53-1003627-04
387
Содержание FastIron SX 1600
Страница 2: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 2 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 16: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 16 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 20: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 20 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 142: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 142 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 150: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 150 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 200: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 200 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 214: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 214 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 350: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 350 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 476: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 476 53 1003627 04 ...
Страница 588: ...FastIron Ethernet Switch Layer 3 Routing 588 53 1003627 04 ...