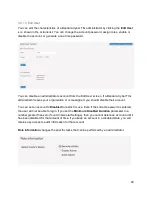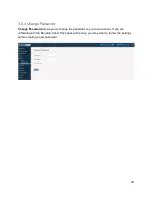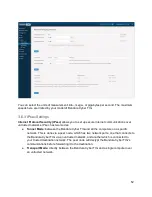
If your IPsec connections pass through your Bandura Cyber TIG’s bridge ports, keep these in
mind:
● Add your outside peer
nodes to an Allowed
Exception
List
in a Policy
, and add that
policy to an egress
Resource
Group
.
● In an egress resource group, create Rules
for the Bandura Cyber TIG's administration
interface
, allowing the protocols ESP
(
Encapsulating Security Payload), AH
(Authentication Header), ICMP
or ICMPv6
(Internet Control Message Protocol, versions
4 and 6), and UDP
(User Datagram Protocol) port
500
for the Internet Key Exchange
(IKE) protocol.
● Put your Destination
IP
Address
in an allowed exception list.
● Add ingress or egress rules for the Bandura Cyber TIG administration interface for
whatever communications you need with the destination.
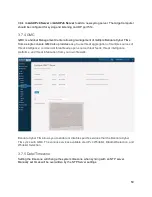
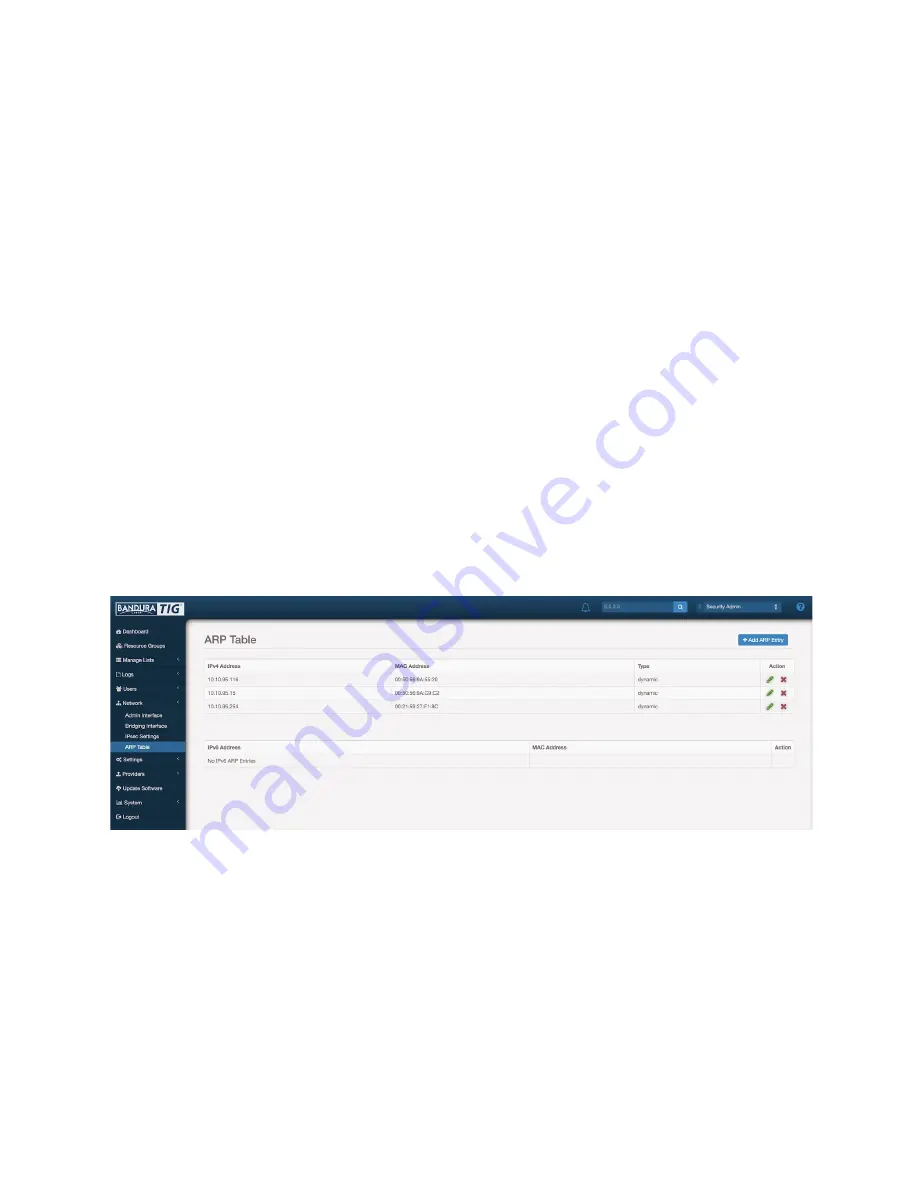
3.6.4 ARP Table
The
Address
Resolution
Protocol
(ARP
)
of IPv4, and the
Neighbor Discovery
Protocol
(NDP
)
of IPv6, are used to determine the
Media
Access
Control
(MAC
)
addresses of nodes on
the same network segment as the Bandura Cyber TIG. The Bandura Cyber TIG may know the
internet address of a node, but still cannot communicate with that node until it obtains the MAC
address of its network card.
The Bandura Cyber TIG automatically updates this table whenever it discovers nodes on its
network segment: these are
dynamic
addresses in this table. Entries you manually add to this
table are static, and you can edit or delete them. You cannot edit a dynamic address, and if you
delete a dynamic address, it will reappear if it is still active on your local network segment.
Although ARP or NDP will normally automatically discover these MAC addresses, in some
circumstances you may want to manually place these hardware addresses in this table. If the
local network of the Bandura Cyber TIG administrative port is not secure, you can manually
enter ARP entries of important nodes, such as the default gateway, to prevent spoofing. If you
54