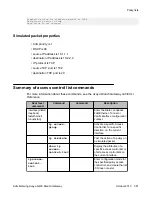
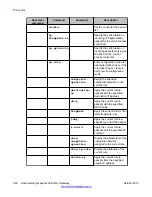
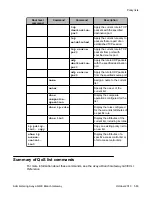
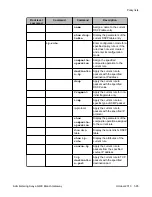
• To assign a name to the list, use the
name
command, followed by a text string,
in the PBR list context. The default name is
list #
<list number>
. For
example:
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802)# name
voice
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802)#
• To assign an owner to the list, use the
owner
command, followed by a text
string, in the PBR list context. The default owner is other. For example:
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802)# owner
tom
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802)#
2. Define PBR rules.
In the PBR list context, enter
ip-rule
, followed by the number of the rule, to define
a rule for the PBR list. Repeat this command to define additional rules. A rule
contains: (i) criteria that is matched against the packet, and (ii) a next hop list. When
a packet matches the criteria specified in the rule, the rule’s next hop list determines
how the packet is routed. Each PBR list can have up to 1,500 rules. The first rule
that matches the packet determines the packet’s routing.
It is important to include a destination address, or range of addresses, in PBR rules
to better classify the traffic to be routed. For an illustration, see
on page 598.
Note:
Leave a gap between rule numbers, in order to leave room for inserting additional
rules at a later time. For example, ip-rule 10, ip-rule 20, ip-rule 30.
The following example creates rule 1, which routes packets going to IP address
149.49.43.210 with a DSCP value of 34 according to next hop list 1. The next step
explains how to define a next hop list. For additional details about PBR rules, see
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802)# ip-rule 1
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802/ip rule 1)# next-hop list 1
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802/ip rule 1)# destination-ip host 149.49.43.210
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802/ip rule 1)# dscp 43
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-PBR 802/ip rule 1)#
Note:
Rules do not include a default next hop list. Thus, if you do not include a next hop
list in the rule, the packet is routed according to destination-based routing, that
is, the ordinary routing that would apply without policy-based routing.
3. Define next hop lists.
Enter
exit
twice to return to general context. In general context, define all the next
hop lists that you have used in PBR rules.
Policy-based routing
590 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway
October 2013
Содержание G430
Страница 1: ...Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway Release 6 3 03 603228 Issue 5 October 2013 ...
Страница 12: ...12 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 ...
Страница 214: ...Ethernet ports 214 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 232: ...System logging 232 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 246: ...VoIP QoS 246 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 250: ...Modems and the Branch Gateway 250 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 302: ...Emergency Transfer Relay ETR 302 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 556: ...IPSec VPN 556 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 604: ...Policy based routing 604 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 610: ...Synchronization 610 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 668: ...Traps and MIBs 668 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...