34
ATmega161(L)
1228B–09/01
• Bit 3
–
ICF1: Input Capture Flag 1
The ICF1 bit is set (one) to flag an input capture event, indicating that the
Timer/Counter1 value has been transferred to the input capture register (ICR1). ICF1 is
cleared by hardware when executing the corresponding interrupt handling vector. Alter-
natively, ICF1 is cleared by writing a logical “1” to the flag. When the SREG I-bit and
TICIE1 (Timer/Counter1 Input Capture Interrupt Enable) and ICF1 are set (one), the
Timer/Counter1 Capture Interrupt is executed.
• Bit 2
–
OCF2: Output Compare Flag 2
The OCF2 bit is set (one) when a compare match occurs between the Timer/Counter2
and the data in OCR2 (Output Compare Register 2). OCF2 is cleared by hardware when
executing the corresponding interrupt handling vector. Alternatively, OCF2 is cleared by
writing a logical “1” to the flag. When the I-bit in SREG and OCIE2 (Timer/Counter2
Compare match InterruptA Enable) and the OCF2 are set (one), the Timer/Counter2
Compare match Interrupt is executed.
• Bit 1
–
TOV0: Timer/Counter0 Overflow Flag
The bit TOV0 is set (one) when an overflow occurs in Timer/Counter0. TOV0 is cleared
by hardware when executing the corresponding interrupt handling vector. Alternatively,
TOV0 is cleared by writing a logical “1” to the flag. When the SREG I-bit and TOIE0
(T i m e r / C o u n t e r 0 O v e rf l o w I n t e rr u p t E n a b l e ) a n d T OV 0 a r e s e t ( o n e ), t h e
Timer/Counter0 Overflow interrupt is executed.
• Bit 2
–
OCF0: Output Compare Flag 0
The OCF0 bit is set (one) when compare match occurs between the Timer/Counter0
and the data in OCR0 (Output Compare Register 0). OCF0 is cleared by hardware when
executing the corresponding interrupt handling vector. Alternatively, OCF0 is cleared by
writing a logical “1” to the flag. When the I-bit in SREG and OCIE0 (Timer/Counter0
Compare match InterruptA Enable) and the OCF0 are set (one), the Timer/Counter0
Compare match Interrupt is executed.
External Interrupts
The external interrupts are triggered by the INT0, INT1, and INT2 pins. Observe that, if
enabled, the interrupts will trigger even if the INT0/INT1/INT2 pins are configured as out-
puts. This feature provides a way of generating a software interrupt. The external
interrupts can be triggered by a falling or rising edge or a low level (INT2 is only an edge
triggered interrupt). This is set up as indicated in the specification for the MCU Control
Register – MCUCR (INT0/INT1) and EMCUCR (INT2). When the external interrupt is
enabled and is configured as level triggered (only INT0/INT1), the interrupt will trigger as
long as the pin is held low.
MCU Control Register –
MCUCR
The MCU Control Register contains control bits for general MCU functions.
• Bit 7
–
SRE: External SRAM Enable
When the SRE bit is set (one), the external data memory interface is enabled and the
pin functions AD0 - 7 (Port A), A8 - 5 (Port C), ALE (Port E), WR, and RD (Port D) are
activated as the alternate pin functions. The SRE bit overrides any pin direction settings
in the respective data direction registers. See Figure 51 through Figure 54 for a descrip-
tion of the external memory pin functions. When the SRE bit is cleared (zero), the
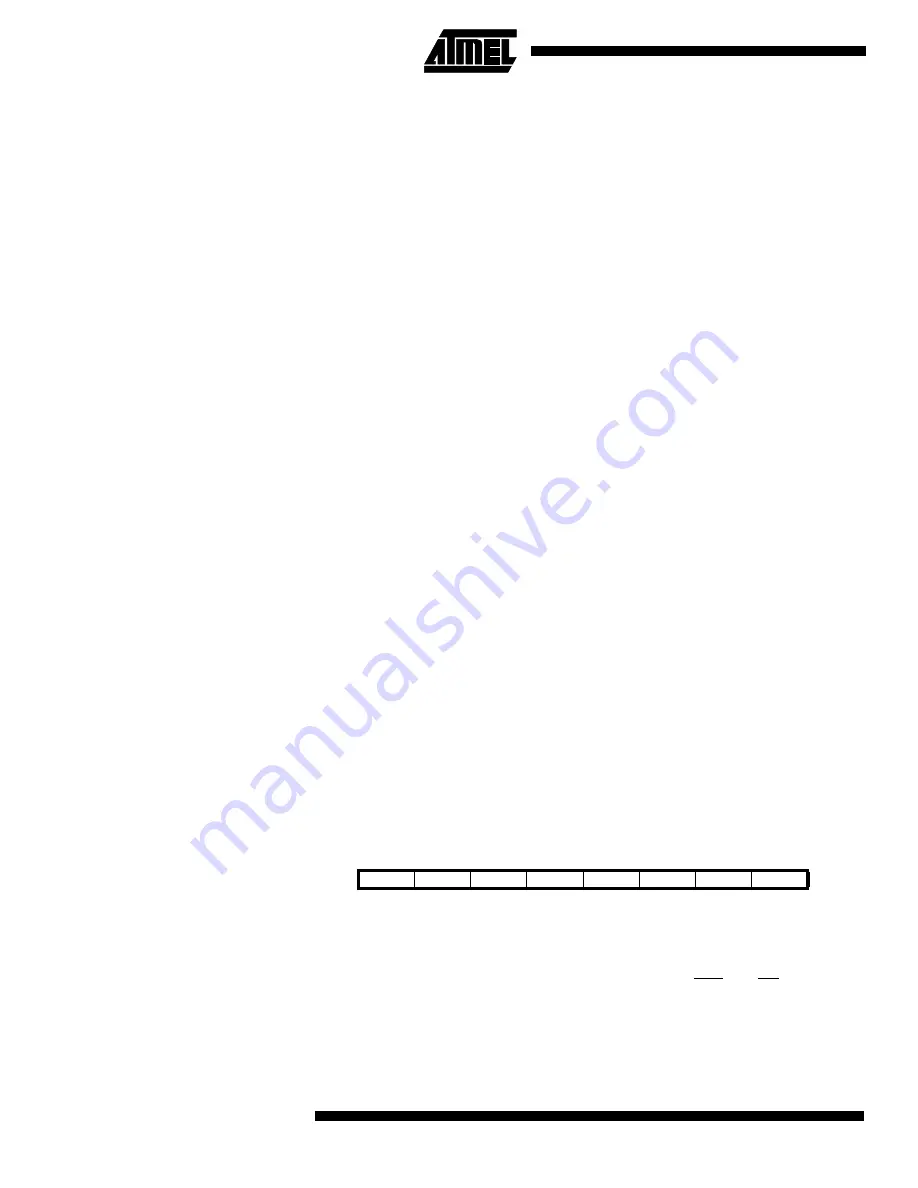
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
$35 ($55)
SRE
SRW10
SE
SM1
ISC11
ISC10
ISC01
ISC00
MCUCR
Read/Write
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Initial Value
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
















































