[AK4675]
MS0963-E-00
2008/05
- 136 -
ミ
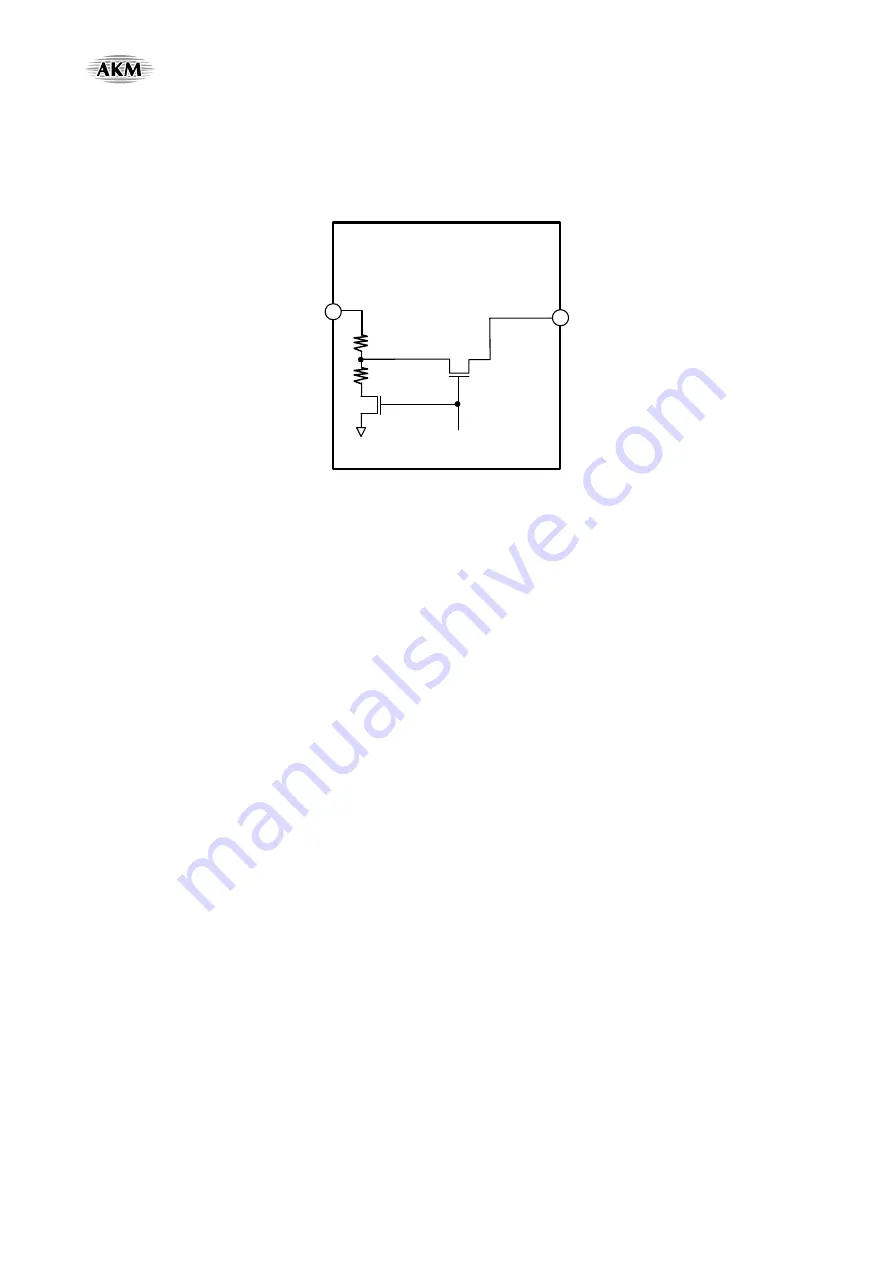
ATT Circuit for Battery Monitor
When BATCPU bit = “1”, the input voltage for the VBATIN pin is divided by the internal resistors R1 (7.5k) and R2
(2.5k). The VBATO pin outputs the internally divided voltage. When BATCPU bit = “0”, the VBATO pin goes to Hi-Z.
This block can operate even if PMVCMA=PMOSC bits = “0”.
R1=7.5K
R2=2.5K
VBATIN pin
BATCPU bit
AK4675
VBATO pin
Figure 103. ATT circuit for Battery Monitor
ミ
Serial Control Interface
(1) I
2
C Bus Control Mode
The AK4675 supports the fast-mode I
2
C-bus (max: 400kHz). Pull-up resistors at SDA and SCL pins should be connected
to (DVDD+0.3)V or less voltage.
(1)-1. WRITE Operations
shows the data transfer sequence for I
2
C-bus mode. All commands are preceded by START condition. HIGH
to LOW transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH indicates START condition (
). After the START
condition, a slave address is sent. This address is 7 bits long followed by the eighth bit that is a data direction bit (R/W).
Addresses for CODEC and HP/SPK-Amp are fixed (
). If the slave address matches that of the AK4675, the
AK4675 generates an acknowledge and the operation is executed. The master must generate the acknowledge-related
clock pulse and release the SDA line (HIGH) during the acknowledge clock pulse (
). R/W bit value of “1”
indicates that the read operation is to be executed. “0” indicates that the write operation is to be executed.
The second byte consists of the control register address of the AK4675. The format is MSB first, and the most significant
1-bit is fixed to “0” (
). The data after the second byte contains control data. The format is MSB first, 8bits
). The AK4675 generates an acknowledge after each byte has been received. Data transfer is always
terminated by a STOP condition generated by the master. LOW to HIGH transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH
defines a STOP condition (






























