Chapter 2
73
Programming Fundamentals
SCPI Language Basics
Special Characters in Commands
Parameters in Commands
There are four basic types of parameters: booleans, keywords, variables
and arbitrary block program data.
OFF|ON|0|1
(Boolean)
This is a two state boolean-type parameter. The
numeric value 0 is equivalent to OFF. Any numeric
value other than 0 is equivalent to ON. The numeric
values of 0 or 1 are commonly used in the command
instead of OFF or ON. Queries of the parameter always
return a numeric value of 0 or 1.
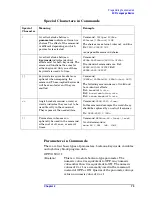
Special
Character
Meaning
Example
|
A vertical stroke between
parameters
indicates alternative
choices. The effect of the command
is different depending on which
parameter is selected.
Command:
TRIGger:SOURce
EXTernal|INTernal|LINE
The choices are external, internal, and line.
Ex:
TRIG:SOURCE INT
is one possible command choice.
A vertical stroke between
keywords
indicates identical
effects exist for both keywords. The
command functions the same for
either keyword. Only one of these
keywords is used at a time.
Command:
SENSe:BANDwidth|BWIDth:OFFSet
Two identical commands are: Ex1:
SENSE:BWIDTH:OFFSET
Ex2:
SENSE:BAND:OFFSET
[ ]
keywords in square brackets are
optional when composing the
command. These implied keywords
will be executed even if they are
omitted.
Command:
[SENSe:]BANDwidth[:RESolution]:AUTO
The following commands are all valid and
have identical effects:
Ex1:
bandwidth:auto
Ex2:
band:resolution:auto
Ex3:
sense:bandwidth:auto
< >
Angle brackets around a word, or
words, indicates they are not to be
used literally in the command.
They represent the needed item.
Command:
SENS:FREQ <freq>
In this command example the word <freq>
should be replaced by an actual frequency.
Ex:
SENS:FREQ 9.7MHz
.
{ }
Parameters in braces can
optionally be used in the command
either not at all, once, or several
times.
Command:
MEASure:BW <freq>{,level}
A valid command is:
meas:BW 6 MHz, 3dB, 60dB