164
C
HAPTER
10: RSTP C
ONFIGURATION
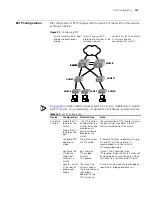
The comparison process of each Switch is as follows.
■
Switch A:
AP1 receives the configuration BPDU from Switch B and finds out that the local
configuration BPDU priority is higher than that of the received one, so it
discards the received configuration BPDU. The configuration BPDU is processed
on the AP2 in a similar way. Thus Switch A finds itself the root and designated
bridge in the configuration BPDU of every port; it regards itself as the root,
retains the configuration BPDU of each port and transmits configuration BPDU
to others regularly thereafter. By now, the configuration BPDUs of the two
ports are as follows:
Configuration BPDU of AP1: {0, 0, 0, AP1
}
.
Configuration BPDU of AP2: {0, 0, 0, AP2
}
.
■
Switch B:
BP1 receives the configuration BPDU from Switch A and finds that the received
BPDU has a higher priority than the local one, so it updates its configuration
BPDU.
BP2 receives the configuration BPDU from Switch C and finds that the local
BPDU priority is higher than that of the received one, so it discards the received
BPDU.
By now the configuration BPDUs of each port are as follows: Configuration
BPDU of BP1: {0, 0, 0, AP1
}
, Configuration BPDU of BP2: {1, 0, 1, BP2
}
.
Switch B compares the configuration BPDUs of the ports and selects the BP1
BPDU as the optimum one. Thus BP1 is elected as the root port and the
configuration BPDUs of Switch B ports are updated as follows.
The configuration BPDU of the root port BP1 retains as {0, 0, 0, BP1
}
. BP2
updates root ID with that in the optimum configuration BPDU, the path cost to
root with 5, sets the designated bridge as the local Switch ID and the
designated port ID as the local port ID. Thus the configuration BPDU becomes
{0, 5, 1, BP2
}
.
Then all the designated ports of Switch B transmit the configuration BPDUs
regularly.
■
Switch C:
CP2 receives from the BP2 of Switch B the configuration BPDU {1, 0, 1, BP2
}
that has not been updated and then the updating process is launched. {1, 0, 1,
BP2
}
.
CP1 receives the configuration BPDU {0, 0, 0, AP2
}
from Switch A and Switch
C launches the updating. The configuration BPDU is updated as {0, 0, 0, AP2
}
.
By comparison, CP1 configuration BPDU is elected as the optimum one. The
CP1 is thus specified as the root port with no modifications made on its
configuration BPDU. However, CP2 will be blocked and its BPDU also remains
the same, but it will not receive the data (excluding the STP packet) forwarded
from Switch B until spanning tree calculation is launched again by some new
events. For example, the link from Switch B to C is down or the port receives a
better configuration BPDU.
Содержание 400 Family
Страница 12: ......
Страница 16: ...14 ABOUT THIS GUIDE ...
Страница 58: ...56 CHAPTER 2 PORT OPERATION ...
Страница 68: ...66 CHAPTER 3 VLAN OPERATION ...
Страница 98: ...96 CHAPTER 5 NETWORK PROTOCOL OPERATION ...
Страница 124: ...122 CHAPTER 6 IP ROUTING PROTOCOL OPERATION ...
Страница 156: ...154 CHAPTER 8 ACL CONFIGURATION ...
Страница 218: ...216 CHAPTER 11 802 1X CONFIGURATION ...
Страница 298: ...296 CHAPTER 13 PASSWORD CONTROL CONFIGURATION OPERATIONS ...
Страница 336: ...334 APPENDIX B RADIUS SERVER AND RADIUS CLIENT SETUP ...