Chapter 11 Spanning Tree Protocol
GS-2724 User’s Guide
108
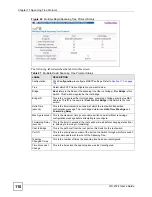
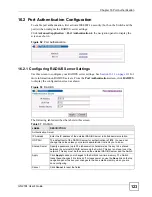
Figure 44
Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26
Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Status
Click
Status
to display the
MRSTP Status
screen (see
Tree
This is a read only index number of the STP trees.
Active
Select this check box to activate an STP tree. Clear this checkbox to disable an
STP tree.
Bridge Priority
Bridge priority is used in determining the root switch, root port and designated port.
The switch with the highest priority (lowest numeric value) becomes the STP root
switch. If all switches have the same priority, the switch with the lowest MAC
address will then become the root switch. Select a value from the drop-down list
box.
The lower the numeric value you assign, the higher the priority for this bridge.
Bridge Priority determines the root bridge, which in turn determines Hello Time,
Max Age and Forwarding Delay.
Hello Time
This is the time interval in seconds between BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Units)
configuration message generations by the root switch. The allowed range is 1 to
10 seconds.
Max Age
This is the maximum time (in seconds) a switch can wait without receiving a BPDU
before attempting to reconfigure. All Switch ports (except for designated ports)
should receive BPDUs at regular intervals. Any port that ages out STP information
(provided in the last BPDU) becomes the designated port for the attached LAN. If it
is a root port, a new root port is selected from among the Switch ports attached to
the network. The allowed range is 6 to 40 seconds.
Summary of Contents for GS-2724
Page 1: ...www zyxel com GS 2724 Ethernet Switch User s Guide Version 3 70 4 2007 Edition 1 ...
Page 2: ......
Page 7: ...Safety Warnings GS 2724 User s Guide 7 ...
Page 8: ...Safety Warnings GS 2724 User s Guide 8 ...
Page 22: ...Table of Contents GS 2724 User s Guide 22 ...
Page 30: ...List of Tables GS 2724 User s Guide 30 ...
Page 32: ...32 ...
Page 36: ...Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch GS 2724 User s Guide 36 ...
Page 40: ...Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection GS 2724 User s Guide 40 ...
Page 46: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Overview GS 2724 User s Guide 46 ...
Page 48: ...48 ...
Page 58: ...Chapter 4 The Web Configurator GS 2724 User s Guide 58 ...
Page 64: ...Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example GS 2724 User s Guide 64 ...
Page 70: ...Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics GS 2724 User s Guide 70 ...
Page 84: ...84 ...
Page 94: ...Chapter 8 VLAN GS 2724 User s Guide 94 Figure 36 Port Based VLAN Setup All connected ...
Page 126: ...Chapter 16 Port Authentication GS 2724 User s Guide 126 ...
Page 130: ...Chapter 17 Port Security GS 2724 User s Guide 130 ...
Page 136: ...Chapter 18 Classifier GS 2724 User s Guide 136 Figure 58 Classifier Example ...
Page 139: ...Chapter 19 Policy Rule GS 2724 User s Guide 139 Figure 59 Policy ...
Page 145: ...Chapter 20 Queuing Method GS 2724 User s Guide 145 ...
Page 146: ...Chapter 20 Queuing Method GS 2724 User s Guide 146 ...
Page 152: ...Chapter 21 VLAN Stacking GS 2724 User s Guide 152 ...
Page 166: ...166 ...
Page 183: ...Chapter 27 DHCP GS 2724 User s Guide 183 Figure 89 DHCP Relay Configuration Example ...
Page 184: ...Chapter 27 DHCP GS 2724 User s Guide 184 ...
Page 186: ...186 ...
Page 210: ...Chapter 31 Syslog GS 2724 User s Guide 210 ...
Page 224: ...Chapter 36 Routing Table GS 2724 User s Guide 224 ...
Page 228: ...228 ...
Page 262: ...Chapter 38 Introducing Commands GS 2724 User s Guide 262 ...
Page 296: ...Chapter 42 IEEE 802 1Q Tagged VLAN Commands GS 2724 User s Guide 296 ...
Page 300: ...Chapter 44 Routing Domain Command Examples GS 2724 User s Guide 300 ...
Page 304: ...304 ...
Page 312: ...Appendix B Changing a Fuse GS 2724 User s Guide 312 ...
Page 332: ...Appendix E Common Services GS 2724 User s Guide 332 ...
Page 336: ...Appendix F Legal Information GS 2724 User s Guide 336 ...
Page 348: ...Index GS 2724 User s Guide 348 ...