Chapter 1
IPv6 Basic Configuration
Table of Contents
1.1 IPv6 Overview
Internet Protocol version 6 (
) is a new version of the Internet Protocol. The significant
changes from IPv4 to IPv6 are as follows:
l
Expanded addressing capabilities
IPv6 increases the IP address size from 32 bits to 128 bits, to support more levels
of addressing hierarchy, a much greater number of addressable nodes, and simpler
auto-configuration of addresses. The scalability of multicast routing is improved by
adding a "scope" field to multicast addresses. And a new type of address called an
"anycast address" is defined, used to send a packet to any one of a group of nodes.
l
Header format simplification
Some IPv4 header fields have been dropped or made optional, to reduce the
common-case processing cost of packet handling and to limit the bandwidth cost of
the IPv6 header.
l
Improved support for extensions and options
Changes in the way IP header options are encoded allows for more efficient
forwarding, less stringent limits on the length of options, and greater flexibility for
introducing new options in the future.
l
Flow labeling capability
A new capability is added to enable the labeling of packets belonging to particular
traffic "flows" for which the sender requests special handling, such as non-default
quality of service or "real-time" service.
l
Authentication and privacy capabilities
Extensions to support authentication, data integrity, and (optional) data confidentiality
are specified for IPv6.
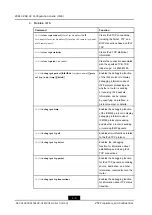
1.2 Configuring IPv6
This procedure describes how to configure the basic functions of IPv6, including ICMPv6
and TCPv6.
1-1
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential