Chapter 4 IPv6 Static Route Configuration
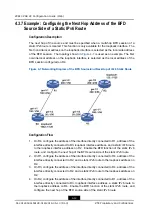
Figure 4-3 Default IPv6 Route Configuration Example
Configuration Flow
1.
Establish the networking structure, and configure the IPv6 address for the interface,
as shown in
2.
Configure the default route, and specify the IPv6 address for gei-4/1 on R2.
Configuration Commands
The configuration on R1 is as follows:
R1(config)#interface gei-2/1
R1(config-if-gei-2/1)#no shutdown
R1(config-if-gei-2/1)#ipv6 enable
R1(config-if-gei-2/1)#ipv6 address 2005::1/64
R1(config)#ipv6 route ::/0 2005::2
/*The IPv6 address configuration on R2 is omitted.*/
Configuration Verification
R1(config)#show ipv6 forwarding route
IPv6 Routing Table:
Headers: Dest: Destination, Gw: Gateway, Pri: Priority;
Codes
: K: kernel, I1: isis-l1, SFN: sf-nat64, R: ripng, AF: aftr, B: bgp,
D: direct, I2: isis-l2, SLN: sl-nat64, O: ospfv3, D6: dhcp, P: ppp,
S: static, N: nd, V: vrrp, A: address, M: multicast, UI: user-ipaddr;
Dest
Owner
Metric
Interface
Pri
Gw
::/0
S
0
gei-2/1
1
2005::2
4.3.4 Example: Configuring FRR for Static IPv6 Route in a Public
Network
Configuration Description
FRR provides backup protection for important nodes or links in the network when they
are invalid to implement fast rerouting, thus minimizing the impact on traffic and restoring
traffic quickly. As shown in
, FRR function is configured for static IPv6 routes in
a public network.
4-7
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential