21
Section 5
Battery Management
Safe, reliable use of all ZOLL devices requires a
well-designed battery management program to ensure
that adequate battery power is always available.
The 6 key steps to developing a battery program are:
1. Obtaining proper equipment.
Plan to have a sufficient number of battery packs and
chargers to insure an adequate supply of fully
charged primary use and spare use batteries.
2. Assigning a responsible individual.
Assign the responsibility to an individual who can
oversee all aspects of the program as well as
educate other ZOLL Monitor/Defibrillator users.
3. Defining battery exchange and charging routines.
Clinical and technical staff should determine desired
use patterns and an optimum sequence to insure
consistent charging and exchange routines.
4. Ensuring sufficient spare battery capability.
A fully-charged spare battery should be kept
immediately available with all ZOLL Monitor/
Defibrillator devices. The availability of more than one
spare battery is recommended in cases where
prolonged or repeated use of the device may be
required, such as long transport situations.
5. Developing backup procedures.
Procedures to maintain appropriate life support (such
as cardiopulmonary resuscitation) should be pre-
planned in the event that a device fails and another
battery or device must be sought.
6. Testing batteries regularly.
Develop a testing schedule as part of your
organization’s battery management program. The
appropriate frequency of testing depends on the age
of the battery pack and the frequency and type of
use. As the battery ages, testing should be more
frequent since failure will occur rapidly at the battery’s
end-of-life. At a minimum, ZOLL recommends testing
every three months. For additional information on
Battery Management, refer to the ZOLL Battery
Management Program (part number 9650-0019).
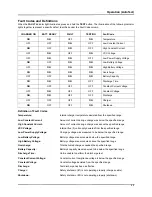
=2//%DWWHU\3DFNV
ZOLL PD 4410/Smart/Smart Ready Battery and XL
Battery Packs are five-cell assemblies of sealed lead-
acid batteries specifically designed for use with all ZOLL
Monitor/Defibrillator devices.
Lead acid battery packs require full recharging after use.
Continuous short cycle recharging will result in reduced
capacity and early battery pack failure.
%DWWHU\/LIH([SHFWDQF\
Frequency of use, number of batteries used, and the
pattern of discharging and recharging batteries
contribute to the loss of battery charge capacity.
Because of this, ZOLL recommends that operators
replace and discard used batteries on a preventive,
scheduled basis. The most effective preventive
replacement interval should be based on anticipated use
patterns, battery pack testing results and experience with
the device in actual operation. ZOLL recommends
battery replacement every eighteen months or sooner.
For more information about such a schedule, contact
your ZOLL Technical Service Representative.
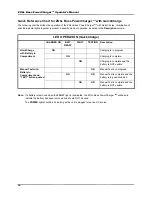
/RZ%DWWHU\0HVVDJH
As individual battery capacity diminishes, the amount of
operating time remaining after a LOW BATTERY
message also diminishes. For newer or lesser-used
batteries, the operating time remaining after this warning
will be significantly longer than the operating time
remaining on batteries that have seen more use. In
either case, this warning will ultimately lead to
defibrillator shut-off, and consequently, the low battery
should be replaced with a fully-charged battery as soon
as possible.
When a LOW BATTERY message is displayed, replace
the battery pack immediately to ensure continuous
operation.
%DWWHU\'LVSRVDO
Place the battery in an acid resistant container. Dispose
of the battery in accordance with federal, state, and local
regulations. Do not incinerate batteries. Batteries should
be shipped to a reclamation facility for recovery of metal
and plastic compounds as the proper method of waste
management.