JOHNSON CONTROLS
18
FORM 155.33-ICOM2.EN.GB
ISSUE DATE: 12/4/2017
SECTION 2 – PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
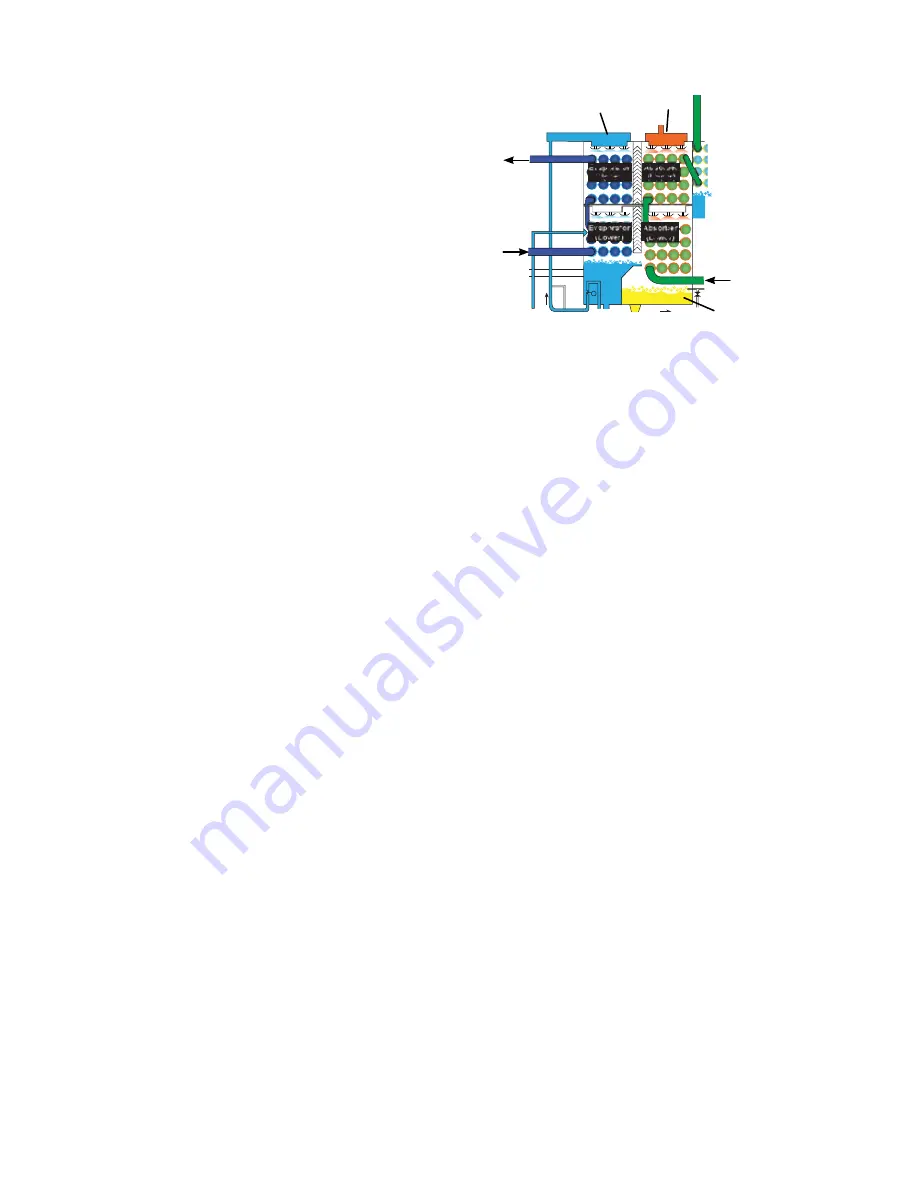
TWO-STEP EVAPORATOR – ABSORBER
The evaporator, as well as the absorber, is split into
two sections. This design allows for lower LiBr solu-
tion concentrations. The lower concentration reduces
pressure, the potential for corrosion, and the risk of
crystallization. It also improves efficiency along with
other advanced components described later.
The two evaporators are in series with respect to the
chilled water flow through the tubes. The chilled wa-
ter flows through the lower evaporator tubes first and
then to the upper evaporator tubes. Each evaporator
operates at a slightly different temperature and pres-
sure. The refrigerant in the lower evaporator boils at
a slightly higher temperature than it does in the upper
evaporator. The chilled water is cooled in two steps as
a result.
The two absorber sections are also split. The strong so-
lution enters the top of the upper absorber and flows
down through the top absorber bundle. It then flows
into the top of the lower absorber section. The strong
solution entering the upper absorber takes advantage
of the lower vapor pressure. The lower pressure allows
the upper evaporator to operate at a lower pressure and
temperature.
When the LiBr solution enters the lower absorber sec-
tion it is diluted due to the refrigerant vapor that boiled
off in the upper evaporator. At this lower concentration,
the solution vapor pressure would not be sufficient to
provide an evaporator pressure low enough to satisfy
the leaving chilled water design. However, the lower
evaporator is the first step of the chilled water cooling
cycle. The dilute solution’s vapor pressure is enough to
maintain the required temperature and pressure in the
lower evaporator.
The cooling tower water enters the lower absorber sec-
tion first. This keeps the vapor pressure of the weaker
solution as low as possible.
Both the refrigerant (water) and LiBr dispersion sys-
tem are gravity fed and made of stainless steel.
LG4
Evaporator
(Upper)
Absorber
(Upper)
Absorber
(Lower)
Evaporator
(Lower)
LD19980_a3
Chilled
Water
In
Cooling
Water
In
Chilled
Water
Out
Refrigerant
Concentrated
LiBr
Dilute (weak)
Solution Out
PLATE TYPE HEAT EXCHANGERS
The four plate
solution heat exchangers (the high tem-
perature solution heat exchanger, the low temperature
solution heat exchanger), and the low temperature LTG
refrigerant condensate heat exchanger; waste hot wa-
ter heat exchanger allow the unit to operate more ef-
ficiently.
The diluted (weak) lithium bromide solution leaving
the absorber section is pumped through various plate
type heat exchangers before it enters the high tempera-
ture generator and low temperature generator sections.
These plate type heat exchangers provide cycle effi-
ciency by pre-heating the dilute solution. Pre-heating
the dilute solution reduces the load of the driving heat
source in the high temperature generator section. The
concentrated solution flows out of the generators and
back through the various heat exchangers.
The relatively high temperature solution streams from
the two generators are used to pre-heat the weak solu-
tion stream leaving the absorber.
The variable frequency drive on the solution circula-
tion pump, as well as the solution spray pump, helps
achieve superior performance at part loads through
savings in energy consumption.
















































